AIDS - A U.S. Made Monster?
PREFACE
In an extensive article in the Summer-Autumn 1990 issue of
"Top Secret", Prof J. Segal and Dr. L. Segal outline their
theory that AIDS is a man-made disease, originating at
Pentagon bacteriological warfare labs at Fort Detrick,
Maryland. "Top Secret" is the international edition of the
German magazine Geheim and is considered by many to be a
sister publication to the American Covert Action Information
Bulletin (CAIB). In fact, Top Secret carries the Naming
Names column, which CAIB is prevented from doing by the
American government, and which names CIA agents in different
locations in the world. The article, named "AIDS: US-Made
Monster" and subtitled "AIDS - its Nature and its Origins,"
is lengthy, has a lot of professional terminology and is
dotted with footnotes.
AIDS FACTS
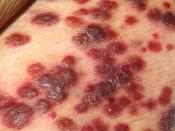
"The fatal weakening of the immune system which has given
AIDS its name (Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome)," write
the Segals, "has been traced back to a destruction or a
functional failure of the T4-lymphocytes, also called
'helper cells`, which play a regulatory role in the
production of antibodies in the immune system."
In the
course of the illness, the number of functional T4-
cells is reduced greatly so that new anti-bodies cannot be
produced and the defenceless patient remains exposed to a
range of infections that under other circumstances would
have been harmless. Most AIDS patients die from
opportunistic infections rather than from the AIDS virus
itself. The initial infection is characterized by diarrhea,
erysipelas and intermittent fever. An apparent recovery
follows after 2-3 weeks, and in many cases the patient
remains without symptoms and functions normally for years.
Occasionally a swelling of the lymph glands, which does not
affect the patient's well-being, can be observed. After
several years, the pre-AIDS stage, known as ARC (Aids-
Related Complex) sets in. This stage includes disorders in
the digestive tract, kidneys and lungs. In most cases it
develops into full-blown AIDS in about a year, at which
point opportunistic illnesses occur. Parallel to this
syndrome, disorders in various organ systems occur, the most
severe in the brain, the symptoms of which range from
motoric disorders to severe dementia and death. This set of
symptoms, say the Segals, is identical in every detail with
the Visna sickness which occurs in sheep, mainly in Iceland.
(Visna means tiredness in Icelandic). However, the visna
virus is not pathogenic for human beings. The Segals note
that despite the fact that AIDS is transmitted only through
sexual intercourse, blood transfusions and non- sterile
hypodermic needles, the infection has spread dramatically.
During the first few years after its discovery, the number
of AIDS patients doubled every six months, and is still
doubling every 12 months now though numerous measures have
been taken against it. Based on these figures, it is
estimated that in the US, which had 120,000 cases of AIDS at
the end of 1988, 900,000 people will have AIDS or will have
died of it by the end of 1991. It is also estimated that the
number of people infected is at least ten times the number
of those suffering from an acute case of AIDS. That in the
year 1995 there will be between 10-14 million cases of
AIDS and an additional 100 million people infected, 80
percent of them in the US, while a possible vaccination will
not be available before 1995 by the most optimistic
estimates. Even when such vaccination becomes available, it
will not help those already infected. These and following
figures have been reached at by several different mainstream
sources, such as the US Surgeon General and the Chief of the
medical services of the US Army. "AIDS does not merely bring
certain dangers with it; it is clearly a programmed
catastrophe for the human race, whose magnitude is
comparable only with that of a nuclear war", say the Segals.
"They later explain what they mean by "programmed," showing
that the virus was produced by humans, namely Dr. Robert
Gallo of the Bethesda Cancer Research Center in
Maryland. When proceeding to prove their claims, the Segals
are careful to note that:
"We have given preference to the investigative results of
highly renowned laboratories, whose objective contents
cannot be doubted. We must emphasize, in this connection,
that we do not know of any findings that have been published
in professional journals that contradict our hypotheses."
DISCOVERING AIDS
The first KNOWN cases of AIDS occurred in New York in 1979.
The first DESCRIBED cases were in California in 1979. The
virus was isolated in Paris in May 1983, taken from a French
homosexual who had returned home ill from a trip to the East
Coast of the US. One year later, Robert Gallo and his
co-workers at the Bethesda Cancer Research Center published
their discovery of the same virus, which is cytotoxic. ( i.e
poisonous to cells ) Shortly after publishing his discovery,
Gallo stated to newspapers that the virus had developed by a
natural process from the Human Adult Leukemia virus, HTLV-1,
which he had previously discovered. However, this claim was
not published in professional publications, and soon after,
Alizon and Montagnier, two researchers of the Pasteur
Institute in Paris published charts of HTLV-1 and HIV,
showing that the viruses had basically different structures.
They also declared categorically that they knew of no
natural process by which one of these two forms could have
evolved into the other. According to the professional
"science" magazine, the fall 1984 annual meeting of the
American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS),
was almost entirely devoted to the question of: to what
extent new pathogenic agents could be produced via human
manipulation of genes. According to the Segals, AIDS was
practically the sole topic of discussion.
THE AIDS VIRUS
The Segals discuss the findings of Gonda et al, who compared
the HIV, visna and other closely-related viruses and found
that the visna virus is the most similar to HIV. The two
were, in fact, 60% identical in 1986. According to
findings of the Hahn group, the mutation rate of the HIV
virus was about a million times higher than that of similar
viruses, and that on the average a 10% alteration took place
every two years. That would mean that in 1984, the
difference between HIV and visna would have been only 30%,
in 1982- 20%, 10% in 1980 and zero in 1978. "This means,"
say the Segals, "that at this time visna viruses changed
into HIV, receiving at the same time the ability to become
parasites in human T4-cells and the high genetic instability
that is not known in other retroviruses. This is also
consistent with the fact that the first cases of AIDS
appeared about one year later, in the spring of 1979."
"In his comparison of the genomes of visna and HIV," add the
Segals, "Coffin hit upon a remarkable feature. The env
(envelope) area of the HIV genome, which encodes the
envelope proteins which help the virus to attach itself to
the host cell, is about 300 nucleotides longer than the same
area in visna. This behaviour suggests that an additional
piece has been inserted into the genomes of the visna virus,
a piece that alters the envelope proteins and enables them
to bind themselves to the T4-receptors. BUT THIS SECTION
BEHAVES LIKE A BIOLOGICALLY ALIEN BODY, which does not
match the rest of the system biochemically.
The above mentioned work by Gonda et al shows that the HIV
virus has a section of about 300 nucleotides, which does not
exist in the visna virus. That length corresponds with what
Coffin described. That section is particularly unstable,
which indicates that it is an alien object. According to the
Segals, it "originates in an HTLV-1 genome, (discovered by
Gallo-ED) for the likelihood of an accidental occurrence in
HIV of a genome sequence 60% identical with a section of the
HTLV-1 that is 300 nucleotides in length is zero." Since the
visna virus is incapable of attaching itself to human T4
receptors, it must have been the transfer of the HTLV-1
genome section which gave visna the capability to do so. In
other words, the addition of HTLV-1 to visna made the
HIV virus. In addition, the high mutation rate of the HIV
genome has been explained by another scientific team,
Chandra et al, by the fact that it is "a combination of two
genome parts which are alien to each other BY ARTIFICIAL
MEANS rather than by a natural process of evolution, because
this process would have immediately eliminated, through
natural selection, systems that are so replete with
disorders." "These are the facts of the case," say the
Segals. "HIV is essentially a visna virus which carries an
additional protein monomer of HTLV-1 that has an epitope
capable of bonding with T4 receptors. Neither Alizon and
Montagnier nor any other biologist know of any natural
mechanism that would make it possible for the epitope to be
transferred from HTLV-1 to the visna virus. For this reason
we can come to only one conclusion: that this gene
combination arose by artificial means, through gene
manipulation."
THE CONSTRUCTION OF HIV
"The construction of a recombinant virus by means of gene
manipulation is extraordinarily expensive, and it requires a
large number of highly qualified personnel, complicated
equipment and expensive high security laboratories.
Moreover, the product would have no commercial value. Who,
then," ask the Segals, "would have provided the resources
for a type of research that was aimed solely at the
production of a new disease that would be deadly to human
beings?" The English sociologist Allistair Hay (as well as
Paxman et al in "A Higher Form of Killing"-ED), published a
document whose authenticity has been confirmed by the US
Congress, showing that a representative of the Pentagon
requested in 1969 additional funding for biological warfare
research. The intention was to create, within the next ten
years, a new virus that would not be susceptible to the
immune system, so that the afflicted patient would
not be able to develop any defense against it. Ten years
later, in the spring of 1979, the first cases of AIDS
appeared in New York. "Thus began a phase of frantic
experimentation," say the Segals. One group was working on
trying to cause animal pathogens to adapt themselves
to life in human beings. This was done under the cover of
searching for a cure for cancer. The race was won by Gallo,
who described his findings in 1975. A year later, Gallo
described gene manipulations he was conducting. In 1980 he
published his discovery of HTLV. In the fall of 1977, a P4
(highest security category of laboratory, in which
human pathogens are subjected to genetic manipulations)
laboratory was officially opened in building 550 of Fort
Detrick, MD, the Pentagon's main biological warfare research
center. "In an article in 'Der Spiegel`, Prof. Mollings
point out that this type of gene manipulation was still
extremely difficult in 1977. One would have had to have a
genius as great as Robert Gallo for this purpose, note the
Segals." Lo and behold. In a supposed compliance with the
international accord banning the research, production and
storage of biological weapons, part of Fort Detrick was
"demilitarized" and the virus section renamed the
"Frederick Cancer Research Facility". It was put under the
direction of the Cancer Research Institute rican citizens were exposed
to dangerous doses of radioactivity. Some of them were
prisoners who had volunteered, but they also included
residents of old-age homes, inmates of insane asylums,
handicapped people in nursing homes, and even normal
patients in public hospitals; most of them were subjected to
these experiments without their permission. Thus the
'barbaric past` is not really a thing of the past."
"It is remarkable that most of these experiments were
carried out in university institutes and federal hospitals,
all of which are named in the report. Nonetheless, these
facts remained secret until 1984, and even then a
Congressional committee that was equipped with all the
necessary authorization needed two years in order to bring
these facts to life. We are often asked how the work on the
AIDS virus could have been kept secret. Now, experiments
performed on a few dozen prisoners in a laboratory that is
subject to military security can be far more easily kept
secret than could be the Manhattan Project."