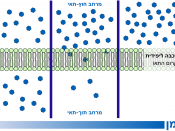
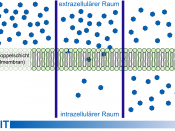
Every cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane. The cell membrane is selectively permeable- only certain substances can cross it freely. The structure of the membrane allows materials to move across it by 2 main means: active and passive transport. Password transport involves two processes: Diffusion and Osmosis. Passive transport allows some substances such gases and water to move into and out of the cell without using energy. Active transport includes processes such as "ion pumps", "exocytosis" and "phagocytosis". Molecules such as sucrose's are moved against their concentration gradient using active transport - this requires the use of energy. A concentration gradient exists whenever two areas have different concentrations of a substance.
Diffusion is the random movement of particles. It is the process by which liquid or gas particles spread from where they are numerous ( high concentration) to where they are scarce ( low concentration) until they are evenly distributed.
Cells use diffusion to take in things from their environment and rid themselves of waste. Diffusion takes place down a concentration gradient. Water, carbon dioxide and other small ions can diffuse freely through cell membranes. Concentration gradients occur in all organisms. Where they do, simple diffusion will transport things around. Nutrients being carried in blood for example will diffuse into those cells that need them. Diffusion is also vital for getting oxygen into cells and carbon dioxide out of them, for example, in humans. Facilitated diffusion occurs when substances move down the concentration gradient by "carrier proteins" in the cell membrane.
Osmosis is also a type of passive transport involving the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane. Water will move by diffusion from an area where there is more of it to an area where there is a less of it. This results in...