Assumptions: Hugo's Hats produces fashion hats for both male and female customers, price per hat ã100. Trades as a Private Limited Company and started trading as an e-business in 1995.
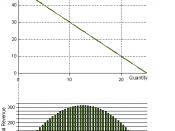
Market Structure is the degree of competition the business faces. There are four market structures as illustrated in figure 1.
Figure 1
Perfect competition is a theoretical model, it does not exist. It is assumed that there are many buyers and sellers, the goods being sold are homogeneous and there is perfect knowledge in the market.
Monopolistic competition is when goods are slightly differentiated in some way, either by advertising or branding or by local production.
Oligopoly is when a few suppliers dominate the market.
Monopoly is when one supplier dominates 25% or more of output.
The following are the main characteristics of Monopolistic competition in which Hugo's Hats are competing:
There are quite a large number of firms, as a result, Hugo's hat has only a small share of the market and, therefore, its actions are unlikely to affect its rivals to any great extent.
There is freedom of entry of new firms into the industry. If any firm wants to set up a business of making hats, it is free to do so.
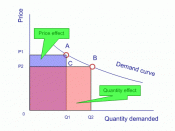
Product Differentiation: Hugo's Hats are producing hats and providing customer service that is in some way different from its rivals. The demand curve is downward sloping, i.e. elastic, as customers are given more choice from different suppliers in the market.
Profits are maximised: In the short run, Hugo's Hat are producing where marginal costs (change in total costs from one extra hat produced) equals marginal revenue (change in total revenue from selling one more hat).
Total cost equals total of variable costs and fixed costs.
Total revenue is quantity sold, Q multiplied by price, P.