Catalysis is of importance to today's chemical industry. There are only a small number of chemical processes that are still conducted without the use of a catalyst. Catalysts are use in an array of applications from the production of consumer goods to the protection of the environment. The approach involves a wide number of specific competencies of solid state chemistry, analytical chemistry, physical chemistry, kinetics and rheology. The fundamental aspects in the preparation of heterogeneous catalysts starting from catalyst design up to the catalyst in its final form are briefly reviewed. The literature will also be treating mechanisms of catalyst deactivation. Mechanisms of catalyst deactivation are many; nevertheless, they can be classified into six distinct types: (1) poisoning, (2) fouling, (3) thermal degradation, (4) vapor compound formation accompanied by transport, (5) vapor-solid and/or solid-solid reactions, and (6) attrition/crushing. Finally the characterization of the catalyst is necessary at every stage of development.
Product quality in commercial productions is aided with appropriate testing, and the first step in any diagnosis of process problems is to measure changes that have occurred. It is vital that accepted techniques for determining these characteristics be established as an adjunct to research design, preparation, testing, and manufacture.
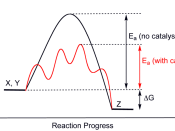
2. IntroductionDefinition of catalyst is, ÃÂA substance that increases the rate at which a chemical reaction approaches equilibrium without itself being permanently involved in the reaction .ÃÂ Mainly, the catalyst speeds up the kinetics of the reaction towards thermodynamic completion by introducing a less difficult path for molecules to follow.
The catalyst properties that have to be considered include selectivity, activity, crush strength, abrasion resistance and resistance to fluid flow . As a result the design of a catalyst involves both the active phase and support. Typical forms of industrial catalysts include powder, pellets, rings, spheres, extrudates or granules, as...