Coronary Artery Disease and
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Coronary Artery Disease
a type of blood vessel disorder that is included in the general category of atherosclerosis.
The term atherosclerosis means "fatty much" and "hard".
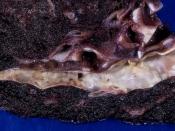
It begins as soft deposits of fat that harden with age and is often referred to as hardening of the arteries.
The atheromas (fatty deposits) have a preference for the coronary arteries.
Etiology and Patho
Atherosclerosis is the major cause of CAD.
Characterized by a focal deposit of cholesterol and lipids, primarily within the intimal wall of the artery.
Plaque formation is the result of complex interactions between the components of the blood and elements forming the vascular wall.
Endothelial lining can be altered as a result of chemical injuries such as hyperlipidemia or high-sheer stress, such as HTN.
There is evidence that some viral and bacteria infections play a role in damaging endothelium by causing a local inflammatory response.
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a non-specific marker of inflammation and is increased in patients with CAD.
Chronic exposure to CRP triggers the rupture of plaque.
With endothelium alteration, platelets are activates and they release a growth factor that stimulates smooth muscle proliferation that entraps lipids, which are calcified over time and form an irritant to the endothelium in which platelets adhere and aggregate.
Thrombin is generated and fibrin formation and thrombi occur.
Endothelial replication is normal slow in adults, but in the presence of HTN & hyperlipidemia, increased cell turn-over lead to transient repeated denuding of the endothelium.
Developmental stages
CAD takes many years to develop.
When it becomes symptomatic, the disease process is usually well advanced.
Stages of development are: fatty streak, raised fibrous plaque resulting from smooth muscle cell proliferation and complicated lesion.
1) Fatty streak
a. Earliest lesion characterized by lipid-filled smooth muscle cells.