International Environment of Business (IB 2180)
Culture's influence, the market impact
Introduction
Culture consists of specific learned norms based on attitudes, values and beliefs which exist in every society. Attitudes and values differ from one country to another resulting in different cultural norms. Therefore, whether it be selling products or organizing, financing and managing its global operations, these differences will affect every firm operating on a global basis.
Impact
The cultural impact on international management is reflected by the basic beliefs and behaviors of people. Firms conducting businesses globally have to deal with clients, strategic partners, distributors, and competitors with different cultural mindsets. By nature, managerial work is a "cultural bound" job, thus, national culture affects all level of operations-from interpersonal communication to formulation of strategy. Differences in cultural values often result in varying management practices. For instance, a person's class or status within a society is dictated by how the particular culture values the person in comparison to others.
"Social stratification" (the ways in which ranking is determined) varies substantially from country to country and affects various business functions such as employment practices. An organization's recruitment, promotion, compensation and redundancy policies differ from one country to another.
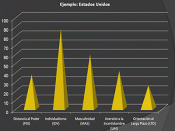
Research conducted by Geert Hofstede shows how national culture affects the values at the workplace. His studies clearly indicated that "work related values are not universal and underlying values persist when a multinational company tries to impose the same norms on all its foreign interests." The four dimensions of culture that Hofstede used in explaining how and why people from various cultures behave, are discussed below.
He employed 'power distance' to indicate the extent to which a society accepts the unequal distribution of power in institutions and organizations. Countries like Argentina and Spain (where power distance is high), inequality is accepted and...