Composites Coursework
Design and Analysis of a Laminated Composite Tube
Abstract
This report details the process for the design of a composite laminate tube, the software package 'MathCAD' was used to determine a lamina design with a configuration that avoids mechanical failure under loading conditions. It was also used to obtain twist angles and maximum stresses for specific lamina wind up angles. The report will provide analysis of the methods used to obtain these criteria.
Aim
Use a Mathcad script to determine the procedure used during the manufacture of a wound laminate composite tube and to assess its validity for use in stress and strain analyses.
Introduction
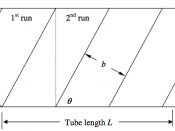
Figure 1 A developed view of a tape-wound cylindrical tube
The laminates of the composite tube adopted a [ñ/ò/ñ/ò] layup with a winding angle range between [-75, -45] or [+45, +75], these tapes were cut from a UD pre-peg sheet onto a 50mm mandrel.
Tape widths were dependant on the winding angles in order to avoid gaps or overlaps as a result of winding onto the mandrel; this would affect the part performance or decrease material efficiency respectively.
The thickness of the pre-peg sheet is 0.25mm and the finished tube should be at a length of 300mm.
Material
Material properties of the carbon-epoxy (SE 84LV/HSC/300g/400mm/37%/1 blue) used to constrict the composite where as follows:
E1 (GPa) | E2 (GPa) | G12 (GPa) | ý12 | ÃÂ*1t (MPa) | ÃÂ*1c (MPa) | ÃÂ*2t (MPa) | ÃÂ*2c (MPa) | ÃÂ*12 (MPa) |
236 | 5 | 2.6 | 0.25 | 3800 | 689 | 41 | 117 | 69 |
Table 1 Carbon-epoxy prepreg properties
A composite material is a material made from two or more constituents with significantly different physical or chemical properties. There are two main categories of constituent materials, matrix and reinforcement. At least one material of each...