DIABETES MELLITUS
Diabetes Mellitus-
Is a multisystem disease related to abnormal insulin production, impaired insulin utilization, or both. Diabetes Mellitus is a serious health problem throughout the world. It is the 5th leading cause of death in the U.S. It is the leading cause of heart disease, stroke, adult blindness, and nontraumatic lower limb amputations.
Etiology and Pathophysiology
Current theories link the cause of diabetes, singly or in combination, to genetic, autoimmune, viral, and environmental factors (obesity, stress). Regardless of its cause, diabetes is primarily a disorder of glucose metabolism related to absent or insufficient insulin supplies and/or poor utilization of the insulin that is available. The two most common types of diabetes are classified as type I or type II diabetes mellitus. Gestational diabetes and secondary diabetes are other classifications of diabetes commonly seen in clinical practice
Normal Insulin Metabolism
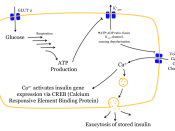
Insulin is a hormone produced by the B cells in the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas.
Under normal conditions, insulin is continuously released into the bloodstream in small pulsatile increments (a basal rate), with increased release (bolus) when food is ingested. The activity of released insulin lowers blood glucose and facilitates a stable, normal glucose range of approximately 70 to 120 mg/dl. The average amount of insulin secreted daily by and adult is approx. 40 to 50 U, or 0.6 U/kg of body weight.
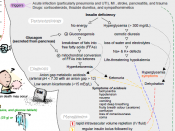
Other hormones (glucagons, epinephrine, growth hormone, and cortisol) work to oppose the effects of insulin and are often referred to as counterregulatory hormones. These hormones work to increase blood glucose levels by stimulating glucose production and output by the liver and by decreasing the movement of glucose into the cells. Insulin and the these counterregulatory hormones provide a sustained but regulated release of glucose for energy during food intake and periods of fasting...