Diabetes mellitus Leading cause of blindness in the U.S. under 60 years of age.
Diabetic patients have vessel atherosclerosis, putting them at risk for CAD, CVA.
DM causes peripheral symmetric polyneuropathy. Neuropathy causes autonomic dysfunction, leading to delayed gastric emptying, a tonic bladder, and impotence.
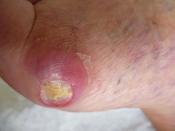
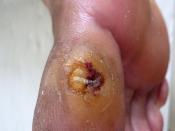
Skin changes: Slow wound healing, acanthosis nigricans and necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum.
IDDM, type 1 diabetes: Occurs in young people of normal or low weight.
Little or no endogenous insulin secretion.
An autoimmune disease with a few genetic components.
Features: polydipsia, polyuria, and rapid weight loss.
Untreated IDDM results in diabetic ketoacidosis.
Labs: the plasma glucose more than 200 mg per deciliter after 75 grams of oral glucose (oral glucose tolerance test) and more than 200 mg per deciliter between 0 and two hours after oral glucose.
Patients may have ketonemia of ketonuria or both.
Treatment: diet is key to management---55 to 60 percent carbohydrates, 30 percent from fat, 10 to 15 percent protein.
Regular meal intervals .
Insulin may be delivered by injection or pump. Regular is short acting and is used before meals.
Non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, type 2 Middle-aged or older people were overweight.
Insulin levels are normal or high but tissues are resistant; delayed and psoas secretion from the pancreas is also present frequently.
Account for 90 percent of diabetes in the United States mostly found in African-Americans, Hispanics, and Pima Indians.
Type II has strong genetic components.
Exercise and weight loss decrease the risks.
Untreated NIDDM can lead to hyperosmolar nonketotic states. The Features: polyuria polydipsia; ketonuria and weight loss are rare.
Other presentations: blurred vision, poor wound healing, fatigue and candidal vaginitis Labs: glycosylated hemoglobin and fructosamine Treatment: diet, weight loss, self-monitoring, oral hypoglycemic agents (sulfonylureas) stimulates insulin secretion -- -- -- glipizide, glyburide (second generation agents...