DNA MICROARRAY TECHNOLOGY
One of the most exciting nucleic acid analysis techniques is microarrays or DNA chips. They provide a radically different approach to large-scale analysis and qualification of genes and gene expression patterns. A microarray consist of an ordered arrangement of hundreds or thousands of DNA sequences such as oligonucleotides or cDNAs deposited onto a solid surface approximately 1,2 x 1,2 cm. The microarray technique is based on hybridization of nucleic acids. Sequence complementarity provides the hybridization between two single-stranded nucleic acid molecules, one of which is immobilized on a matrix.
There are two variants of the chips; cDNA microarrays and oligonucleotides arrays. Both of them can be used to analyze gene expression patterns, however there are important differences between them. They differ in the size of the arrayed nucleic acids.
In cDNA microarrays, long DNA molecules are immobilized by high-speed robots on a solid surface such as membranes, glass or silicon chips.
Sample DNAs are amplified by PCR and usually are longer than 100 nucleotides. This type of arrays is used mostly for large-scale screening and expression studies.
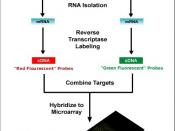
The oligonucleotide arrays are employed either by in situ light-directed chemical synthesis or by conventional synthesis followed by immobilizations on a glass substrate. Those with short nucleic acids (up to 25 nucleotides) are useful for the detection of mutations and expression monitoring, gene discovery and mapping. The general scheme of an array experiment is shown in the following figure.
CONSTRUCTION OF MICROARRAYS
The following diagram shows the main steps of microarray construction.
CONSTRUCTING PCR PRODUCT-BASED DNA MICROARRAYS
1.Primer Design: The first step is to design primers to amplify certain regions of genomic DNA. The simplest way to design primers is to use the beginning and ending regions of a specific open reading frames.
2. PCR Amplification: The...