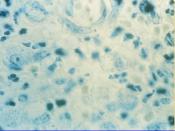
Calymmatobacterium Granulomatis, (scientific name) is a specific species of bacteria that causes Granuloma Inguinale, (most commonly called Donovanosis). Donovanosis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that affects the groin area. Donovanosis usually forms as genital lesions, which are slow to heal, develop, and cause little or no pain. Unfortunately, the disease is usually ulcerative.
Interestingly, Donovanosis is caused by Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, a gram-negative pleomorphic bacillus. The bacterium is rod shaped.
Donovanosis is mostly transmitted through sex, but also is transmitted through a fecal route or by passage through an infected birth canal. The disease is mildly contagious, and repeated exposure may be necessary for clinical infection to occur.
The symptoms of Donovanosis are split into four different groups, depending on the type of Donovanosis, (Considering the fact that there are four different types). Most symptoms appear between 1 and 16 week after contact.
Ulcerovegetative type (most common): painless ulcers that spread at a very speedy rate.
The ulcers are typically a bright beefy red and bleed very easily, sometimes just from touch. Most ulcers are between one-half and two inches long. Occasionally, they range from two to four inches long. It is very rare that an ulcer would reach over four inches.
Nodular type: Soft, often pruritic, red nodules arise at the site of inoculation and eventually ulcerate, presenting a bright red granulating surface. These tend to be the most painful of all.
Cicatricial type: Dry ulcers evolve into cicatricial plaques and may be associated with lymphedema.
Hypertrophic or verrucous type (relatively rare): This proliferative reaction with formation of large vegetating masses may resemble genital warts.
Extreme Elephantitis of the genitals in later stage lesions is very common, and very painful.
Donovanosis has the ability to spread to other areas of the body. Some areas it most commonly...