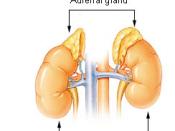
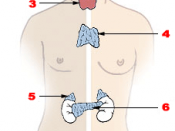
The endocrine system regulates the body's major continuous and prolonged processes including reproduction; growth and development; cellular metabolism and energy; blood balance of nutrients, electrolytes and water; and the immobilization of body defenses against stressors (things that cause wear and tear on the body's physical and mental resources). It is made up of eight different glands located strategically throughout the body: the ovaries (In men, the testes), adrenals, pancreatic Islets, thyroid, parathyrold, pineal, pituitary and the hypothalamus, which Is also part of the nervous system. Besides these major organs, the system Includes pockets of hormone-producing cells In tissues in the small Intestine, heart, kidneys and stomach. The endocrine system develops and begins producing hormones by the end of the second trimester of fetal.
In the order of endocrine command, the hypothalamus is the body's CEO, orchestrating the events of the rest of the endocrine system. The hypothalamus controls autonomic reflexes (such as the activity of the heart and smooth muscles), and it houses the body's "thermostat" and biological clock, which maintains the body's rhythm of 24 hour sleep-wake cycles.
The somewhat mysterious pineal gland also has a role in biological timekeeping being an organ sensitive to retinal response to light. The pineal gland1 believed to coordinate fertility hormones, produces melatonin, the hormone known for Its sleep-triggering ability.
The hypothalamus also initiates part of the adrenal stress response, causing the pituitary to secrete the hormone that travels to the adrenal glands to stimulate secretion of cortisol, DHEA and aldosterone. The hypothalamus also Initiates 'the female cycle by producing gonadtropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which signals the pituitary to secrete foliici stimulating hormone (F$H). FSH stimulates the ovaries to secrete estrogen, the sex hormone that stimulates development of breast, uterine and ovarian tissue (and in synthetic HRT forms is associated with excessive...