BIOLOGY NOTES TERM 1 2003
MICROSCOPY
Ocular - lens used for magnification (usually x10)
Objectives - lenses used for magnification
Lower powerx4
Medium powerx10
High powerx40
Course adjustment - focuses image, moves focus quickly
Fine adjustment - focuses image, moves focus slowly
Stage - specimens are placed here
Condenser - focuses light
Iris diaphragm - controls amount of light passing through the specimen
TOTAL MAGNIFICATION
=
OCULAR MAGNIFICATION X OBJECTIVE MAGNIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
Taxonomy
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Scientific names
Binomial system uses GENUS and SPECIES names
Keys
1)branching Keys
these keys use a tree diagram to sort out specimens
2)Dichotomous Keys
These keys use a series to pairs of questions to sort out specimens
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
Five Kingdoms
Monera - bacteria
Protsita - single celled (have a nucleus)
Fungi - mushrooms/toadstools etc (do not photosynthesise)
Plants - contain chlorophyll and photosynthesise
Animals - multi-cellular life forms that rely on other means for nutrition
Animal Kingdom
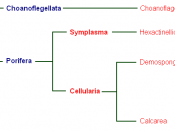
Phylum porifera
÷Sponges
÷Primitive
÷No organs or systems
÷Basically, a group of cells with a common collective purpose
÷Sponges are filter feeders
Phylum Cnidaria
÷Anemones, corals and jelly fish
÷Possess stinging cells called cnidocytes
÷Possess a very simple digestive system, a sac with one opening
÷Corals secrete a hard calcareous (calcium carbonate) skeleton
÷2 main body forms:
1)Polyp
Include corals and anemones
2)Medusa
Include jellyfish
Phylum platyhelminthyes
÷Tapeworms
÷Very simple digestive system (may be absent)
÷Well developed reproductive system
÷Can be free living or parasitic
÷Tapeworms and flukes (par.)
÷Planarians (free living)
Phylum Nematoda
÷Roundworms, heartworm, hookworm, pinworm
÷Parasitic or free living
÷Digestive system with 2 openings
Phylum Mollusca
÷Molluscs snails, slugs, oysters, cuttlefish, octopus, abilone
÷Soft muscular body often with a hard calcareous shell (sometimes internal)
÷Well developed eyes
÷Complex nervous system
Phylum Annelida
÷Segmented worms, earth worms, leeches, marine worms
÷Body is divided into segments, can possess appendages (sep. marine worms)
Phylum Arthropoda
÷Hard exoskeleton with segments
Class Crustoces
÷Crustaceans: crabs, lobsters, prawns, shrimps, crayfish, barnacles, water fleas
Class Chelicerata
÷Arachnids: spiders, ticks, mites, scorpions
Class Diplopoda
÷Millipedes
Class Chilopoda
÷Centipedes
Class Insecta
÷Insects
÷Possess a ventral nerve chord (complex nervous system)
÷Largest phylum in animal kingdom, 800 000 species
Phylum Echinodermata
Starfish, sea urchin, sea cucumber
÷Spiny skinned
÷Radially symmetrical
÷Internal calcareous skeleton
÷Tube feet moved by water/fluid pressure
Phylum Chordata
÷Dorsal nerve chord
÷Most advanced body design
Subphylum Urochordata
÷Only possess dorsal nerve chord as larvae
e.g. sea squirt
Subphylum Cehpalochordata
÷Possess dorsal nerve chord right through to adult hood
÷Do not possess a backbone
e.g. lancelet
Subphylum Vertebrata
÷Possess a backbone
÷Commonly called vertebrates
Class Chondricthyes
÷Sharks, rays
÷Cartilage skeleton
÷2 chambered heart
class Osteichthyes
÷True bony fish
÷Skeleton made of bone
÷What we commonly call fish, seahorse, eel
Class Amphibia
÷Frogs, toads, salamanders
÷Undergo metamorphosis from young to adult, tadpole - frog
÷Lay eggs and can only reproduce in water
÷Possess lungs
Class Reptilia
÷Lizards, snakes, crocodiles, turtles, tortoises
÷Lay eggs but reproduce on land
÷3 chambered heart
Class Aves
÷Birds, e.g. penguin, emus, ostriches
÷Possess feathers and beaks
÷Lay eggs
÷Birds are homeothermic (have a constant body temp.)
÷Have a 4 chambered heart
Class Mammalia
÷Mammary glands that secrete milk
÷4 chambered heart
÷Homeothermic
Monotremes
÷Platypus, echidna
÷Lay eggs
Marsupials
÷Kangaroos, wombat, koala
÷Have a pouch
÷Give birth to extremely underdeveloped young that need to live in pouch
Placental Mammals
÷Give birth to well developed young
÷Unborn young nurtured by a placenta
Plant Kingdom
Phylum tracheophyta
÷Vascular plants, possess special tissue that conducts water nutrients
÷This allows these plants to attain a greater size
Class Filicopsida
÷Ferns
Class Cycadopsida
÷Cycads
Class Ginkgopsida
÷Maidenhair
Class coniferopsida
÷Pine trees, etc
÷Possess cones
Class angiospermopsida
÷Flowering plants
Subclass Monocatyledonae
Grasses, lilies, orchids and palms
Subclass Dicotyledonae
Most of the flowering trees and shrubs
Phylum Algae
÷Simple structure, does not extend into leaves, stems and roots
÷Most live underwater
÷Some are microscopic single-celled plants and others are giant and leathery
Phylum Bryophyta
÷Mosses, liverworts
÷Small, less than 40cm tall
÷Often bear structures resembling stems and leaves
÷Lack well developed vascular tissue and true roots
KINGDOM ANAMALIA
PORIFERA CNIDARIA PLATYHELMINTHES NEMATODA MOLLUSCA ANNELIDA ARTHROPODA ECHINODERMATA CHORDATA
UROCHORDATA CEPHALOCHORDATA VERTEBRATA
Crustacea chelicerata diplopoda chilopda insecta
Chondricthyes Ostechthyes Amphibia Reptilia Aves Mammalia
Arachnids/Kingcrabs
BIOLOGY - TERM 2
REVISION NOTES
ECOSYSTEMS
DEFINITIONS:
Population - a group of organisms of the same kind living in a particular place
Community - is the group of all organisms living in a particular place.
Ecosystem - is the combination of living things and the physical environment.
Abiotic - non-living component of an organisms surroundings
Biotic - living component of an organisms surroundings.
Habitat - an organisms immediate surroundings.
Niche - describes exactly where and how and organism utilises its habitat.
Food chain -
Food web -
Trophic levels - describes the position that an organism fill in a food chain or web
Autotroph - a self-feeder or producer
Heterotroph - a consumer.
Decomposer -
Energy Flow:
In ecosystems:
÷The suns is the primary source of energy in any ecosystem
÷Plants harness only .1% of the sun's energy that reaches the earth
÷This small percentage of energy is all that keeps life, as we know it in existence
Through food webs:
÷In order for energy to reach top order consumers in a food web, it has to pass through a number of different trophic levels
÷This means that the energy passed from one organism feeds another
The nature of energy:
÷Energy is not created or destroyed
÷Energy is converted from one form to another
÷When energy is converted, some of it is lost to the system
÷When energy is converted in a food web, some of it is lost as heat.
÷Therefore energy transfer is never 100% efficient.
The loss of energy along a food chain:
Solar energy
Biomass:
÷The total mass of living tissue in an ecosystem
÷A biomass pyramid describes the amount of biomass at each trophic level in an ecosystem
÷There is less energy available to sustain biomass as we progress up the food chain. Because of this, biomass decreases thus forming the typical shape of a biomass pyramid.
CYCLES
Water:
÷The suns energy powers this cycle
÷Precipitation is run off from streams, rivers and lakes, rain, snow, sleet, dew, etc
÷Water is evaporated from lakes, streams, rivers and oceans, etc.
÷Water is transpired from plants.
Carbon:
CARBON IN ATMOSPHERE
PLANTS
ANIMALS
DECOMPOSERS
SOME CARBON LOCKED
IN FOSSIL FUELS
Nitrogen:
Phosphorous:
RELATIONSHIPS - SYMBIOSIS
Mutualism:
÷Involves two organisms living closely together with both species benefiting from this association
÷E.g clown fish & anemone, clown fish gets protection (naturally immune to stings of anemone) anemone receives food scraps from clown fish and gets cleaned as well
Commensalism:
÷Involves one species gaining benefit form living closely with another species, which is neither harmed nor benefited.
÷E.g barnacles on whales, barnacle receives protection and feeding opportunities while the3 whale is neither harmed nor benefited.
Parasitism:
÷Involves one species gaining nutrition at the expense or detriment of another species.
÷Parasite does not kill its host outright but rather enables it to survive for as long as possible
÷Endoparasites (live inside hosts) e.g. tapeworm
÷Ectoparasites (live on outer surfaces of host) e.g. tick, leech, strangler fig
Competition:
÷Involves organisms competing for the same resource
÷Organisms involved can be from the same species or from different species
÷Resources competed for include: food, shelter, territory, mates, etc
÷E.g foxes competing for hares or rainforest or trees competing for sunlight
Predator/prey:
÷Involves one species feeding on another
÷E.g dingo eats bandicoot or kangaroo eats grass
EVIRONMENTAL CHANGE
Human factors:
÷Land clearing
÷Erosion
÷Pollution
Natural changes
Primary succession:
÷Occurs when living things colonise new land such as in a volcanic eruption
÷Bacteria and lichens are normally the first organisms that can live on bare rock
÷As organisms progressively colonise an area, they change the environment, thus making it suitable for new species
÷Sometimes when organisms change an environment, it is no longer suitable for themselves
÷The changing environment leads to a change in species, which is in essence, what a succession is.
Secondary succession:
÷Occurs in an already established ecosystem
÷These successions are often caused by natural disasters like floods or fires
÷Although they do not involve a total change in species they often involve a marked change ad new species take hold in the affected area.
CLASSIFICATION
Taxonomy:
÷Kingdom
÷Phylum
÷Class
÷Order
÷Family
÷Genus
÷Species
Scientific names:
÷Binomial system uses GENUS and SPECIES names
Keys:
1)Branching Keys
These keys use a tree diagram to sort out specimens
2)Dichotomous Keys
These keys use a series to pairs of questions to sort out specimens
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS:
÷Five Kingdoms:
÷Monera - bacteria
÷Protsita - single celled (have a nucleus)
÷Fungi - mushrooms/toadstools etc (do not photosynthesise)
÷Plants - contain chlorophyll and photosynthesise
÷Animals - multi-cellular life forms that rely on other means for nutrition
Humans:
Phylum Chordata
÷Dorsal nerve chord
÷Most advanced body design
Subphylum Vertebrata
÷Possess a backbone
÷Commonly called vertebrates
Class Mammalia
÷Mammary glands that secrete milk
÷4 chambered heart
÷Homeothermic
Placental Mammals
÷Give birth to well developed young
÷Unborn young nurtured by a placenta