Throughout the advancing technology of today, the human culture is becoming futuristic with science and all of its components. Genetically modifying foods presents positive opportunities in agriculture and human health. Furthermore, more scientifically advanced modifications that select genetically superior plants, have enhanced the yield of crops, improved storability, and increased disease resistance. To simply remove genes from one organism and transfer them to another is generally harmless if we take appropriate precautions. This often debated issue holds many objections. Moreover, one may claim that modifying genes at all is unnatural and evaluates a sufficient risk to many different organisms and species. However, the current technology we possess provides us with the capabilities to go beyond our limits. Why draw the line here?
Genetically modifying foods presents positive and beneficial opportunities. In most cases, we are not eating those genes. By the time a genetically engineered corn plant has been processed into corn oil, virtually none of the genes or the proteins they produce are left in the food (Nutrition Action Healthletter, 2001).
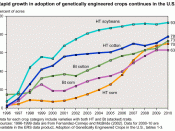
Transferring genes from one plant or animal to another provides an advantageous outcome to this production. A better resistance to weeds, pests, and diseases is produced as well as better yield and a more efficient use of land. Additionally, altering genetics in foods contributes to a better texture, flavour, and nutritional value of a product. Therefore, there is a longer shelf life and less herbicide or other chemicals are used in the production of genetically modified foods, which provides a healthier option and an increased selection for the consumer. Biotechnology is going to help solve problems that we face going into the next century such as reduction of allergies, development of more nutritious foods, and an increased nutritional production to feed a growing population (McLaughlin, 1999). Subsequently,