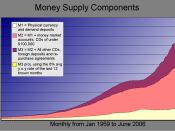
The economic indicator, money supply, is a statistic of the money amount in the United States. There are three categories which include portions of the money supply that is more liquid than the next measure; M1, M2, M3. To control this supply there is the Federal Reserve Bank, who has three methods to control the supply of money into the economy. The first is the buying and selling of US treasury bonds and notes. The second is raising or lowering the federal funds rate. And the third is lowering or raising the reserve requirements. Each one of these methods will decrease or increase the amount of money circulating in the economy.
The money supply has three ways in which to control the money supply, but the money supply itself is part of a bigger method used to control the economy. This method uses economic indicators, or their statistics, to predict and discover how well the economy is performing now and in the future.
There are three categories within this larger group as well; they are leading, lagging and coincidental. A leading indicator is one of a statistical series, which reliably turn up or down before the general economy does. The next type is the lagging indicator, which is really useless in predicting the future because these are factors of the economy that lag behind in relation to economic activity; there changes occur after the overall economy has changed. And the final indicators are the coincidental, which follow the pace of the current economic trends. The Fed uses all of these, some more than others, to steer the county's economy in the right path, and out of recession and inflation.
The money supply is created when banks loan out their reserves to clients, which in turn spend the money on goods...