Fundamentals of Macroeconomics
1 |
6 |
Fundamentals of Macroeconomics
A description of the following terms:
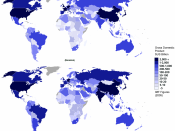
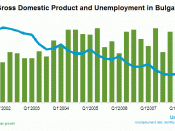
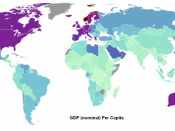
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Real GDP
Nominal GDP
Unemployment rate
Inflation
Interest rate
Gross domestic product is the market worth of goods and services produced in a one year time. This is controlled by the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Real GDP is the market worth of goods and services produced in the financial system confirmed in the prices of a particular year.
Nominal GDP is figures that are gauge by its existing prices.
Unemployment rate is the fraction of individuals in the nation that are willing and able to work but are not employed and receiving unemployment benefit for a stated amount of time.
Inflation is the increase in prices which may result in the loss of the value or currency. The inflation rate is another main factor that the macroeconomist look at when processing calculation.
Inflation is calculated in two ways the gross domestic product and the consumer price index. The Gross Domestic Product and the Consumer Price Index deflator tend to shift in the identical route and vary by a lesser amount of than 1%.
Interest rate is percentage money charged when you borrow money from a financial institution. When the interest rate decrease that mean the purchasing power increase, when the banks make money from the loans they have accumulated that means interest rates will fall in which will increase investment expenditures. When the economy has lower interest rates businesses will assume more asset projects.
The following list below are consider economic activities and a description of how each affects the government, a household, and a businesses and describes the flow of resources from one entity to another for each activity.
Purchasing of groceries:
The nation as...