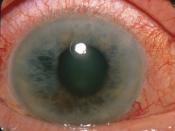
What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of permanent blindness around the world that is preventable. This disease takes away the sense of sight slowly and there are no warning signs most of the time. The damage caused is permanent and cannot be reversed. With the correct eye care there will be little vision loss. Glaucoma is caused by the pressure inside the eye being elevated causing lack of blood flow to the optic nerve, thereby causing the vision loss. There are two main types of glaucoma. There is chronic simple (open-angle) and acute (angle-closure). In chronic simple, the pressure in the eye goes up gradually and vision loss will be over a period of years. In acute the pressure goes up rapidly and medical treatment is needed to preserve the vision. The more common of the two is chronic simple or open-angle. The nerve cells that are lost due to glaucoma are called ganglion cells.
Each of these cells has a long fiber that connects it to the brain. As these cells die, the nerve fibers are then lost. When this happens, the nerve fiber layer gets thinner. This causes an empty space in the optic nerve, which is the "cup" of the optic nerve, to become larger until the nerve is completely gone. This is what the ophthalmologist goes by to determine the amount of damage caused by this disease. (Ritch, and Liebmann, alt.support.glaucoma, 2002).
The definition that is in the encyclopedia is as follows: "an eye disease caused by raised pressure inside the eye." (Webster's Family Encyclopedia, 1989, vol. 5 p. 107).
Glaucoma is the result of a variety of diseases. Bacteria, viral or degenerative factors, do not cause glaucoma. It is caused from a combination of anything that stops the blood flow from...