�PAGE � �PAGE �5� Globular protein, X-ray crystallography
Globular protein, X-ray crystallography
�
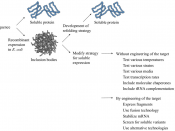
Strategy to purify and characterize a globular protein from bacteria
A bacterium which is a microorganism has a storage f protein inside it. Escherichia coli are one of the bacteria which could be called as protein factory. The two important factors for purifying and characterizing the bacterium protein are the inclusion bodies and cellular metabolism. Some insoluble aggregates which are targeted by protein are called inclusion bodies. Cellular metabolism is directly influenced by the catalytic properties of protein. (Sorensen & Mortensen, 2008)
The amount of raw material and energy which is used for the maintenance of foreign DNA is known as metabolic burden, which is derived from the host metabolism. One of the most important factors which determine the ability of cell to produce a soluble recombinant protein is that there is no link between the metabolic burden and inclusion body formation but both of them are important.
There are number of factors which could help in the metabolic burden and accumulation of the denatured protein.
Bacterium protein could be fold spontaneously, so under normal conditions a cytoplasmic protein subset must be folded. Molecular chaperone is also required during aggregation prone protein. The aggregation during the folding process is prevented by the molecular chaperons. Nascent polypeptide chain helps in the prevention of aggregation. An aggregation of the recombinant proteins is formed by the accumulation of folding intermediates and processing by the molecular chaperons. (Sorensen & Mortensen, 2008)
Some of the techniques which are used to purify and characterize a protein under a given method are given below:
Protein expression at reduced temperature
Strains which are used to improve soluble expression
Modification of cultivation strategies to obtain soluble protein
Folding of recombinant proteins
Interaction partners
There are two important aspects which should be handled carefully: one subset which focuses on the extreme metabolic situation and another subset focus on the structural ability and improving solubility.
�
X-ray Crystallography in Structural genomics
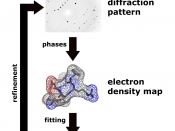
X-ray Crystallography deals with the study of crystals with the help of X-rays. The atomic arrangement of a crystal is determined by the scattering of a beam of X-ray within a crystal. A three-dimensional structure of the density of electrons is given by this process. The process derives mean atomic position, chemical bonds and their disorder. Biological process could be determined with the help of the 3D structure of a molecule. (Nelson, 2003)
X-ray Crystallography determines the 3D structure of RNA and protein molecules in structural genomics projects.� An X-ray beam with high intensity is used in X-ray Crystallography to identify the atomic diffraction pattern of protein. The beam is obtained by the synchrotron radiation. The diffraction data is analyzed after producing a crystal of protein and loaded into the beam line. The structure of large molecules could be solved with the help of X-ray crystallography. The interaction of pharmaceuticals with its protein target which is determined by the scientist uses the X-ray crystallography regularly.
One of its uses is to know, how protein target could be improved by making some changes in its structure. The intrinsic membrane of the protein needs to be soluble in detergents or some other means, which is a challenge for the crystallizing method because the detergents make interferences in the process of crystallization. Ion channel and receptor which are the proteins of great physiological importance are included by the large component of the genome.
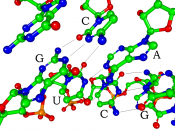
The importance of the structure of different types of RNA molecule could be described in virology. The understanding of different 3D structures of RNA molecules given by X-ray crystallography is important for the formation of anti-viral drug. RNA is an unstable molecule which could be transformed into different disease causing material. (Structural genomics, 2008). Some viruses, such as hepatitis C, flu and HIV use RNA to store genetic information. The 3D structure of RNA derived from the X-ray crystallography is used to identify and describe the presence of the viruses in RNA molecule.
�
References
Nelson, S. A. (September 09, 2003) "X-Ray Crystallography" Retrieved February 25, 2008 from http://www.tulane.edu/~sanelson/eens211/x-ray.htm
Structural genomics, Retrieved February 25, 2008 from http://ec.europa.eu/research/health/genomics/tabs/structural_genomics_en.htm
Golden, B. L. & Gooding, A. R. (1996), "X-ray crystallography of large RNAs: heavy-atom derivatives by RNA engineering" Retrieved February 25, 2008 from http://www.rnajournal.org/cgi/content/abstract/2/12/1295
Sorensen, H. P. & Mortensen, K. K. (2008), "soluble expression of recombinant proteins in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli" Retrieved February 25, 2008 from http://www.microbialcellfactories.com/content/4/1/1
� Structural genomics, Retrieved February 25, 2008 from � HYPERLINK "http://ec.europa.eu/research/health/genomics/tabs/structural_genomics_en.htm" ��http://ec.europa.eu/research/health/genomics/tabs/structural_genomics_en.htm�