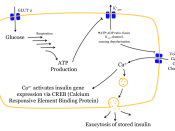
Control Of Blood Glucose
Blood glucose is the primary source of energy in the human body, and is the only source of energy for the brain. The glucose is transported all over the body via the blood plasma and if there is too much present it is stored in the kidneys as glycogen (polysaccharide carbohydrate).
The level of blood glucose has to be maintained by the body. Too higher levels or too lower levels will cause problems in the body. The osmotic properties of the cell will be affected, if there are high amounts of glucose outside the cell and low amounts inside the cell, which will mean there are higher amounts of water inside the cell as there is outside the cell, so water will move out of the cell and the cells will begin to shrink. Another big problem is that the cells will not be able to respire properly as they will not have the correct amounts of energy.
This can be particularly dangerous to the brain cells as their only source of energy comes from glucose. Cells take up the glucose through insulin this is secreted by the Islet B cells (ò cells). When the cells do not secrete enough insulin the body cannot take up the glucose properly and problems will begin to occur.
When the production of insulin in the body starts to break down or if enough is not produced, problems will occur. This problem is classed as a disease Diabetes mellitus (sugar diabetes). There are 2 types of diabetes: type 1, diabetes also referred to as Juvenile- onset diabetes or insulin dependent diabetes. This type of diabetes starts at a young age and can cause many complications. The pancreas doesn't secrete any insulin body this then causes the cues in the body...