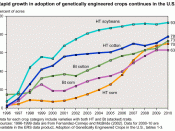
INTRODUCTION:
Genetic modification (GM) is the manipulation of a living organisms' genetic material by the elimination, alteration or addition of specific gene-encoding DNA sequences. Genetic modification often involves the transfer of genetic material from one organism to another so that the recipient may express traits that are naturally characteristic of the donor.
BACKGROUND:
The use of biotechnology to aid the production of crops and livestock has a longstanding history. Genetic modification of plants and animals was practiced through domestication and controlled breeding long before the heritability of traits and the role of DNA was fully understood. Recent advances in our understanding of DNA; since its identification as the 'transforming principle' , the discovery of its double-helical structure and the analysis of its genetic code , have led to major developments within the field of genetics and the advent of genetic engineering. Recombinant DNA technology was successfully implemented to produce the first genetically modified organism (GMO) in 1973 by the combined research of Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen.
Boyer and Cohen engineered a recombinant E. coli bacterium which contained a plasmid vector insert into which a piece of foreign DNA had been spliced. The foreign DNA sequence included a marker coding for resistance to the antibiotics tetracycline and kanamycin, the resultant recombinant organism demonstrated acquired resistance to these antibiotics thus confirming successful integration of the foreign genetic material. In 1980 scientists engineered the first genetically modified animal, a transgenic mouse, and in 1983 the first transgenic plant, an antibiotic resistant tobacco plant was created. Since these pioneering breakthroughs there have been rapid expansions in the production of transgenic organisms particularly for commercial use in medicine, food and agriculture. The first GM food crop to be grown commercially was a tomato dubbed FlavrSavrî created by Calgene, which was put on the US...