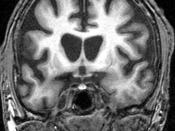
Huntington's disease, often abbreviated as HD, is a brain disease that causes nerve cells in the brain to deteriorate. Dr. George Huntington originally discovered HD in 1872. HD was originally known as Huntington's chorea, coming from a Greek word meaning to dance, which describes some symptoms of HD.
There are three main symptom areas; those are movement, cognitive, and psychiatric. Movement symptoms include sudden muscle spasms, falling down, difficulty speaking, and in later stages difficulty swallowing, which leads to extreme weight loss. Cognitive symptoms include trouble learning new things, difficulty multitasking, trouble prioritizing, and difficult communication in general. Psychiatric symptoms of HD include mostly depression, anxiety, and irritability, OCD with certain activities, delirium, and mania.
Luckily, Huntington's disease is very uncommon. HD appears in about one and every 10,000 Americans. Males and females are equally at risk for inheriting HD. There are about 30,000 known cases in the USA, and 150,000 said to be at risk.
This means that one of their parents had the disease, and they have a 50% chance of being affected.
Today, there is no known treatment for HD. However, there is treatment for the symptoms. Treatment requires counseling and education about the disease of both the family and the patient. Medical treatment must be individualized, since the symptoms are so varied in type and severeness. Depression, a common symptom, can be treated with tricyclic antidepressants. Some types of serotonic agents can treat obsessive-compulsive disorder, another common symptom. Neuroleptics, or drugs that block dopamine receptors, are useful in the treatment of chorea.
Currently, there are five types of research being done on HD: basic neurobiology, clinical research, imaging, animal models, and fetal tissue research. Basic neurobiology uses the HD gene to understand how it causes disease in the human body. In clinical research, investigators observe...