PLANT STRUCTURE
Angiosperms /Magnoliaphyta
Two groups
Dicots and Monocots
Are classified by following features MONOCOTS DICOTS
Seed leaves One cotyledon Two cotyledon
Leave veins Parallel Network of veins usually branched
Stems Random veins (vascular bundles)
Complex arrangement Veins (vascular bundles)are arranged in a ring
Flowers Multiples of three Multiples of four or five
Roots Fibrous root system Taproot system
(long roots)
THE PLANT BODY CONSISTS OF ROOTS AND SHOOTS
The Root System
Root Ankers in the soil
Absorbs and transports minerals and water stores food
Root hairs Is an outgrowth of an epidermal cell
increase the surface area of the root
THE SHOOT SYSTEM
Is made up of stems, leaves and adoptions for reproduction
Stems Are the parts of the plant that are generally above the ground
Supports the leaves and flowers
Transport water minerals and sugar
Nodes Leaves and buds come out
(point which leaves are attached)
Internodes The portion of the stem between nodes
Leaves Main site of photosynthesis
Produces food of plant
apical bud (terminal bud) gives growth and length
(in many plats the terminal bud produces hormones that inhibit growth of the axillary buds)
Axillary buds one in each of the angles formed by a leaf and the stem
are usually dormant
MANY PLANTS HAVE MODIFIED ROOTS AND SHOOTS
Example:
Strawberry Plant Has horizontal stem (runner)
A runner is a means of sexual reproduction
A new plant can emerge form its tip
Iris Plant Have horizontal stems called rhizome(can spread and form new plants)
Store food and have buds
Potato Plant Has rhizomes that end in enlarged structures called tubers (the potato we eat)
Note: modified stem parts of the shoot system potato, iris,
Plant Cells And Tissues Are Diverse In Structure And Function
Central Vacuole Unique to the plant kingdom
Store water
Poisons
Red colored pigments
Waste
Plant cell wall Made up of cellulose
Cell walls that support have a two part cell wall
Primary cell wall The primary wall is laid down first
Secondary cell wall Is more ridged between the plasma membrane and the primary wall
(has lequin)
are harder and tend to be thicker than primary cellwalls
Middle Lamella Hold the primary walls of adjacent cells together (a sticky layer)
Plasmodesmata channels of communication and circulation between adjaacent plant cells
Phloem
2 cells in the phloem
conducting cell
companion cell
Primary cell wall
Secondary cell wall Thicker has lignin
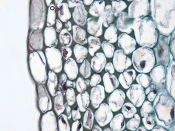
Parenchyma cell (general cell) The most common cell in a plant
No specialization
Relatively small
Have only primary cell walls
Has a thin wall
Has multiple sided (like diamant 25 sides)
Thin wall
Chloroplast
Can have storage vacuoles
Stores starch and sugars
Collenchyma cell Only have a primary wall but thickened
A alive at maturity
Becomes thick and elongated
Function: support plant that are still growing
(found at parameter of stems)
Sclerenchyma cells Rigid secondary cell walls
Hardened with lignin
Mature sclerenchyma cells cannot elongate
They occur only I regions that have stopped growing in length
When mature they are dead
(think of trees wood)
Fiber Is long and slender usually occurs in bundles
Primary walls parenchyma
Secondary wall is sclerenchyma
Hemp is a long fiber
Sclereid Or stone cell is shorter than the Fiber and has a thick irregular and very hard secondary wall
nutshell and seed coats
sclereid is scattered in the soft tissue of a pear
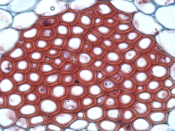
FOOD CONDUCTING CELLS
Two types Both having rigid , lignin-containing secondary cell wass
Tracheids Long cells with tapered ends
Water passes through pits
vessel elements Wider , shorter, less tapered
Note: Chains of tracheids or vessel elements with overlapping ends form a system of tubes that conveys water form the roots to the stems and leaves
The tubes are hollow
Because both tracheids and vessel elements are dead when mature
(the cells also function in support because of their rigid cell walls)
Food conduction cell Also known as sieve tube members
Have thin primary walls
No secondary cell wall
Remain alive during maturity
Xylem Vascular tissue contains water-conducting cells convey water and minerals upward from the roots
Phloem Vascular tissue contains sieve-tube members that transport sugars from leaves or stage tissues to other parts of the pant.
water
sugars (sap )
amino
acids
hormones
there are two cells in the phloem Conducting cell (the large one has no nucleus)
Companion cell with the nucleus
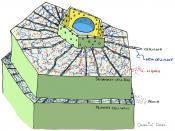
Three tissue systems make up the plants body
Epidermis The skin of the plant
Covers and protects
Defense against physical damage and infectious organisms
stem has no stomates is covered with
root has no cuticle (has root hair coming out)
Ground tissue system Cortex (consists mostly of parenchyma cells) and endodermis (innermost layer of cortex)
Fills the spaces between the epidermis and vascular tissue
Mainly parenchyma cells but usually include some collenchymas and sclerenchyma, Storage
Photosynthesis
Support
has diverse function
Endodermis Controls entry of flow into the vascular tissue
Inside the endodermis - are mainly parenchyma cells
Lateral (axillery bud) meristern creates branch
Pith Part of dicot ground system fills the center of the stem (important I food storage
Guard Cells Regulate the size of the stomata
Vascular tissue system Xylem and phloem
Provides support and transports water and nutrients through the plant
Mesophyll Ground tissue of a leaf
Consists mainly of parenchyma cells
MERISOMATIC TISSUE SYSTEM
Meristem Unspecialized cells that dived and generate new cells and tissues
meristems At the tips of roots
And in the terminal (top)
and axillary buds of shoots
are called apical meristems
1. primary maristems shoot and root tips
result in growth and length - apical merisystem
1. Lateral-meristems
(axilery buds) In lateral buds-branches
Pericycle of roots -branched roots
2. Secondary meristems Vascular cambium
Produce, layers of xylem and poem
Secondary growth
Root cap the very tip of the root
protects the delicate cells