INTRODUCTION
This assignment will review recent articles pertaining to the use of sequential compression devices (SCDs) for the prevention of lower limb problems in conjunction with the lithotomy position during laparoscopic gynaecological surgery. It will discuss the results of the review as they relate to clinical practice and the skills I have acquired in the pre-operative and assessment phases of the patient. I will then address how the information gained will be used to enhance the patient care I deliver.
DISCUSSION
It is current standard practice for patients coming to theatre for laparoscopic Gynaecological surgery to have SCDs sleeves applied by the ward staff. When questioned many staff did not know how to assess the patient to ensure the sleeves fitted correctly or what type of patients should not have SCDs on. They were not aware of the potential complications from positioning for this type of surgery or the problems that could arise from the use of SCDs.
Indeed there were much discussion and conflicting arguments as to the effectiveness of the SCD's for patients in the lithotomy position. Peers and colleagues understanding of the benefits of SCD's ranged from alleviating post operative pain not related to surgical incision, and improving venous return; to effectively reducing the potential for compartment syndrome to occur in the lower limbs. While others thought SCD's had no effect on the patient during their hospital admission.
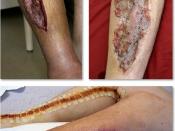
Compartment syndrome occurs when pressure on the tissues within the calf of the leg is sustained for a prolonged period of time, arterial perfusion and circulation to the limb cannot be maintained resulting in swelling of the tissues Mumtaz et al 2002). When a patient is placed in lithotomy position their legs are raised to 90 degrees and the calves and upper thighs are supported by the positioning device.