The major challenges for small to medium sized businesses to remain competitive in e-commerce include; cost, infrastructure and capability issues. The costs may accumulate over time, and evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO) should be our first consideration. This takes into account acquisition costs, operations costs, and control costs. When these costs are identified we can make more accurate cost-benefit analysis. Outsourcing any technical costs could result in cost savings and benefit in experience of the resource provider (Turban et al, p. 629). The infrastructure includes content creation, delivery and management. The major categories are information about the company, products, services, customers, investor relations, press releases, enterprise resource planning (ERP) (including warehouse management systems [WMS]), customer relationship management (CRM), and web site hosting, design, promotion, and information architecture (Turban et al, 2006, p. 677). Attempting to cover all of these areas by a small to medium sized business could exhaust all resources or be impossible.
A small or medium sized business may not be capable of maintaining an e-commerce system by them. The best action plan would be a competitive bidding process that would keep prices lower.
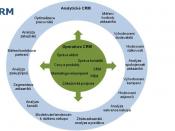
Value added ERP and CRM
ERP is an integration of several software applications. Classic ERP systems comprise modules for operations and corporate services. "A key ingredient of most ERP systems is the use of a single, unified database to store data for the various system modules" (Wikipedia, 2006). ERP systems also offer pre-integrated CRM systems. Examples of packages commonly referred to as ERP systems include: SAP, Oracle (with the companies it took over), The Sage Group, and the Microsoft Dynamics suite of ERP products. Examples of modules in an ERP which formerly would have been stand-alone applications include: Manufacturing, Supply Chain, Financials, CRM, Human Resources, and Warehouse Management (Wikipedia, 2006).
CRM focuses on the interfaces between the firm and its customers: these include activities such as marketing, sales and service. The goal of CRM is to attract and retain customers (Jelassi and Enders, p.161, 614). To be effective, the CRM process needs to be integrated end-to-end across marketing, sales, and customer service (Wikipedia, 2006). "Major CRM vendors are Siebel, Oracle SAP, IBM, and Nortel/Clarify. Smaller players are Vignettee, BroadVision, Onyx, Microstrategy, E.piphany, Roundarch, and KANA" (Turban et al, p. 552).
Implications for HFY
The first things we need to address are if we need to invest in more modern technology to remain competitive, and will we need outside help in order to be successful? CRM and ERP will provide direct results in these areas. HFY will need to be careful while outsourcing some of its technologies. A business could become too dependent on the outside suppliers and lose control over those areas. We will also look at the additional features these companies may try to offer HFY. These could incur more costs to us in the long run. HFY may also find the high fixed costs overwhelming and consider leasing or renting the software needed to defer the costs over time (Jelassi and Enders, p. 66).
Resources
Jelassi, Tawfik and Enders, Albrecht, Strategies for e-Business: Creating Value
through Electronic and Mobile Commerce, Prentice Hall, Pearson Education Limited, 2005
Turban, Efraim; King, David; Viehland, Dennis; Lee, Jae; Electronic Commerce:
A Managerial Perspective, Pearson/Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 2006
Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, (2006). Enterprise resource planning.
Retrieved July 21, 2006 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterprise_resource_planning
Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, (2006). Customer relationship management.
Retrieved July 21, 2006 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Customer_relationship_management