Microeconomic Reform
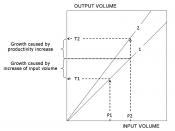
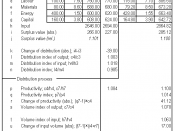
Productivity growth is important for economic growth, the enhancement of employment opportunities, improving export competitiveness, and increasing the resilience of the Australian economy to adverse shocks (P.J. Forsyth, Microeconomic Reform in Australia, 1992). Prior to the 1990s, Australia's productivity growth and overall living standards were relative to the rest of the world, declining rapidly. Since then, Australia has sought to improve the productivity growth of its industries and markets by actively implementing a program of microeconomic reform (MER). Microeconomic reforms are intended to encourage a more efficient use of the nation's resources by making workers and enterprises, both government and private, more responsive to changing circumstances (J. Quiggin, Great Expectations: Microeconomic Reform and Australia, 1996).
Areas that have been subject to reform
Areas that have been subject to MER include (Productivity Commission, Microeconomic Reforms and Australian Productivity: Exploring the Links, 1999):
The labour market - award restructuring, enterprise bargaining, multi-skilling, union amalgamations and more flexible work practices are examples of reforms which aim to improve the skills, flexibility and productivity of the workforce.
Tariffs and protection -tariffs are reduced to provide incentives for local industry to improve quality, productive efficiency and customer satisfaction, and to introduce new products and new technologies. Tax reforms - taxes act as disincentives to productive investments and work. The reduction of high marginal business and personal income taxes, the widening of the tax base and the dividend imputation to prevent double taxation are among the reforms designed to promote efficiency. Infrastructure - Industry needs to be served by efficient transport, communications and energy systems. Reforms to promote efficiency in these areas include deregulation of the aviation industry, change to waterfront work practices, user charges for resources and standardisation of rail links. Financial deregulation - The financial sector was one...