The sea is the most obvious feature of the earth's surface. Approximately seventy percent of this surface is covered by water, in one way or another. Beneath this water are the familiar sands of the beaches, bottoms of bays, and the inshore ocean. Farther offshore this water covers an amazing submarine topography of underwater canyons, trenches, mountains, and plains. Unlike the continents, which are physically separated from one another, the oceans are continuous and interconnected. Since the 'world ocean is continuous'(M.J. Keen) it has similar characteristics throughout. In the early 1870s oceanographers collected seawater samples from all of the seas of the world at a variety of depths. When analyzed, the samples were found to have quite similar characteristics. These findings convinced many that a method of study was needed. The study of oceans was named oceanography.
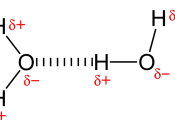
Density, salinity, and temperature are very important concepts in the study of oceanography.
The salinity and temperature of the water influence its density, and the differences in density are the major factor in understanding the formation of currents and the positions of water masses in the sea. In addition, temperature and salinity play major roles in influencing the distribution of plants and animals.
The sediments of the sea floor may be divided into lithogenous, hydrogenous, biogenous, and cosmogenous sediments. Lithogenous sediments are the major sediments on the ocean floor. They are derived from the chemical and mechanical weathering of rocks. Biogenous sediments are composed primarily of the protective outter covering of small marine animals and plants. If these remains comprise at least thirty percent of the sediment it is called an 'ooze'. 'Oozes' were named for the types of organisms that formed them. Hydrogenous sediments form as a result of the chemical reactions that occur in the seawater. These reactions result in the...