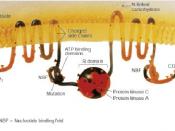
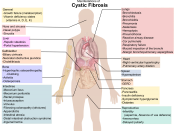
Cystic Fibrosis is a hereditary disease that causes abnormalities in the glands of the exocrine system, affecting the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive functions of sufferers. In our body, exocrine glands discharge various bodily secretions into small ducts (tubes), which lead to the outer surface of the skin or to the interior surfaces of such organs as the stomach and small intestine. In individuals with Cystic Fibrosis, these secretions become abnormally thick, blocking essential ducts. For example, thick mucus in breathing passages in the lungs clogs airways and allows multiplication of bacteria, predisposing to infection; and blocking of the ducts of the pancreas causes malabsorbation of fat. Cystic Fibrosis is the most common fatal inherited disease among whites in the United States, occurring in 1 of every 2500 white (1 in 17000 black) babies. 30,000 children and young adults are currently living with this condition in the USA.
Cystic Fibrosis is generally diagnosed early in life.
Symptoms often recognizable during infancy are: poor weight gain at 4 to 6 weeks; frequent, bulky, foul-smelling, oily stools; protruding abdomen; and slow growth despite large appetite. Soon after, the child will most likely develop regular coughing and wheezing, accompanied by gagging, vomiting, or disturbed sleep. Teenagers most often experience slowed growth, delayed puberty, and declining physical endurance prior to diagnosis. Cystic Fibrosis patients are extremely susceptible to lung disease, and reoccurring pneumonia, bronchitis, atelectasis (lung contractions), enlarged lymph nodes, and sinus infections are the most common traits among CF patients. They have trouble breathing and strong coughs because the mucus blocks the bronchial tubes. The sweat glands of a person with Cystic Fibrosis secrete perspiration containing abnormal amounts of salt, causing easy heat exhaustion, excessive sweating, dehydration, fever, and even formations of salt crystals on the skin.
In extreme cases, infants may...