Parkinson's disease (PD) is a one of the most common neurodegenerative disease. Some of its major features are resting tremors, muscular rigidity, bradykinesia or slowing of movement and postural instability. The disease is associated with the loss of dopamine-generating cells in the substantia nigra(SN), a region of the midbrain. The cause of this cell loss is still unknown; however some hypotheses have been related the cause to genetic factor, environmental toxins and oxidative damage. Scientists have also identified aging as a big risk factor. Even though PD can't be completely cured, the symptoms can be minimized through multiple drug and surgical therapy.
Statistics:
According to Parkinson's Disease Foundation, as many as one million Americans have Parkinson's disease. Approximately 60,000 new cases are diagnosed each year in American alone. An estimated 7 to 10 million people have Parkinson's disease worldwide, affecting all races and cultures. The condition usually develops after the age of 65, but an estimated 4% of those diagnosed are under the age of 50.
In addition, recent research shows a 1 to 1.5 time's higher incidence in males.
Pathology and Pathophysiology:
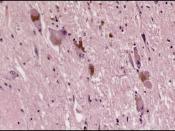
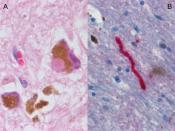
The major anatomical structure that is affected in PD is called substantia nigra( SN), located in the midbrain that plays an important role in control of body movement. SN appears dark due to high levels of the neuromelatin in dopaminergic neurons which is responsible for producing the neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine allows the communication between the substantia nigra and another area of the brain called the corpus striatum and this communications coordinates smooth and balanced muscle movement. In addition, another neurotransmitter called acetylcholine works in conjunction with dopamine to produce smooth movement. In Parkinson's disease, there is greatly reduced activity of these dopaminergic neurons caused by cell death, in the pars compacta region...