Satellite Radio was first introduced to the US in 1992 by the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC). The FCC approved the frequency range of 2.310 to 2.360 GHz in the S band for broadcasting radio throughout North America over the digital audio radio service (DARS). The S band covers the frequency range of 2 to 4 GHz and is usually used for weather radars and communication satellites. Currently XM Radio and Sirius Radio operate on the S band frequency. The L band is similar to the S band but covers the frequency range of .039 to 1.55 GHz. L band is more commonly used for digital audio broadcasting and communication satellites also. Currently World Space Radio uses the L band frequency to supply the majority of the world with satellite radio. (Johnson)When the FCC allowed for private broadcasting over the S band there were four companies that applied for licenses to broadcast on the S band frequency.
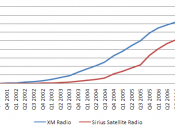
Only two of the four companies received licenses from the FCC to broadcast. The two companies were Sirius Satellite Radio and XM Satellite Radio and they both reportedly paid over 80 million dollars to gain access for the digital satellite transmission. On February 19, 2007, XM and Sirius Radio announced a possible merger deal. The problem the merger is facing is the FCC has mandated that there could not be a monopoly in satellite radio meaning that one company couldn't own both licenses. If the merger is approved the two radio services will combine and create a single Satellite Radio network throughout North America. (Lowry)Currently there are six-satellite radio services worldwide. Satellite radio makes it possible for people to have over 22,000 miles of coverage compared to most radio signals, which usually covers about a 40-mile radius. This allows people nationwide to...