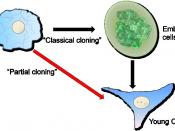
Stem Cells: A Promise for Advancements in Health Care What is a stem cell? It is a cell that is able to divide for a long period of time and gives rise to other cells ("Intermediate"). They are mostly used in human development when a sperm begins fertilizing an egg, creating a single cell that eventually forms into a whole organism. The fertilized egg, now known as totipotent, has the ability to change into extraembryonic tissues and membranes, postembryonic tissues and organs, and the embryo. Two totipotent cells are created after the first cycle of cell division. Four days after the division, a blastocyst (sphere of cells), is formed. The outer layer of cells makes up the placenta and the outer tissues, while the inner mass cells (pluripotent cells) make up almost all of the tissues in the human body. They are able to give rise to most of the cells involved in human development.
Blood stem cells are an example of pluripotent cells. They constantly reload our supply of blood cells, because living without blood stem cells is impossible.
Generating cells and tissues is so far, the most that scientists want the stem cells to achieve. Throughout the past years, people have been donating organs and tissues to hospitals, but the demand for organs and tissues exceeds the number of available transplantation organs. Pluripotent stem cells offer a chance to renew and replace cells and tissues to help cure some diseases such as: diabetes, osteo and rheumatoid arthritis, heart disease, and Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease.
Scientists are hoping to cure weak dying hearts by transplanting healthy heart muscle cells made from human pluripotent stem cells. Scientific studies worked on mice and other animals have shown positive outcomes with the healthy heart muscle cells being transplanted into...