It?s bigger . . . It?s stronger . . . It?s . . .
SUPER FOOD How Genetic Engineering is Changing Your Food Ever since there has been farmers farming there has been a search for stronger foods. Foods to survive pests and weather, and to bring in large harvests, are the traits that these people are looking for. Genetically modified foods are already making some of these dreams come true. In the process, changes in ecology and bioethics have been questioned.
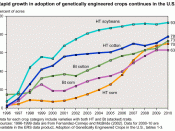
In 1998, 25 percent of U.S. corn was genetically modified (GM). Today more than 45 GM crops have been approved (Wheelwright, Mar.2001). However, the most controversy has been over corn. Starlink corn that is, the corn that set off last September?s recall of many corn-based products. Losses to companies, grain exporters, and Starlink manufacturers is estimated to be over 1billion dollars (Wheelwright, Mar.2001). What could cause such losses? The Starlink corn was only approved for animal consumption.
When it showed up on grocery shelves it had to be recalled immediately in concern that it might trigger allergic reactions. This Starlink is a type of ?Bt? corn. Bt is found in a commercial, spray pesticide. In 1961 it was registered for use in the United States (Wheelwright, Mar.2001). Bt is a natural product but this quality makes it easily removable from the surface of a plant. In the mid 1980?s scientists were able to isolate the gene in Bt that makes it poisonous to insects but harmless to humans, and insert it into plant cells. By 1990 the first successful Bt plant, cotton, was produced (Wheelwright, Mar.2001). After that many varieties were approved for planting and consumption. Today consultation with the Food and Drug Administration is mandatory but labeling products as genetically modified is not required. In addition to...