executive summary
Pakistan State Bank (PSB) has been communicating with the industry regarding this program through the national press, exhibitions, and bulletins in the past.
Today, customers are clearly going global and are demanding quality. Given the stakes involved, it is important for banks to understand all the rules for self-improvement and for doing business in the international marketplace. The Six Sigma has become a basic part any organization.
Competition in banking sector has created both challenges and opportunities for the Pakistani Banking Industry. To succeed, Pakistan must produce the best banking products and provide excellent banking services at the best prices. To do so, we have to follow the best quality management approaches. Pakistani Banks must focus on international standards in order to meet the challenges created by international competition in this sector.
Six Sigma in many organizations simply means a measure of quality that strives for near perfection.
Six Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects (driving towards six standard deviations between the mean and the nearest specification limit) in any process -- from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service.
The fundamental objective of the Six Sigma methodology is the implementation of a measurement-based strategy that focuses on process improvement and variation reduction through the application of Six Sigma improvement projects.
The bank should itself audit its quality processes to verify that it is managing its processes effectively - or, to put it another way, to check that it is fully in control of its activities
In the application of Six Sigma, the business sectors most interested in implementing the eventual standards are the ones who provide experts to develop the standards. Your own interest may be such that you would like to provide input, or even participate in the work
We must find ways to make major breakthroughs in international trade. This is not possible without major changes and improvements in the management systems in our companies. This could be easily done through Six Sigma
It is important that Pakistani banks realize its importance and start implementing this modern system for improvements. Many companies have already started their journey on the road to Certification; but many are finding it difficult to start
The banking culture in Pakistan is undergoing change from traditional informal management practices, to modern formal management
Modern management practices are flourishing in Karachi and Lahore, as many management schools and centers of excellence are located there
Managers in any industry can improve any business operation especially banking operations by applying Six Sigma's DMAIC process -- to Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control the key processes that affect customer satisfaction
The banking industry should determine where improvement is needed, how service can be improved and where operating system breakdowns occur, why they occur and how they can be avoided
The Six Sigma is a general system of product or service quality criteria, which focuses on key elements, such as product functionality, reliability, usability, maintainability, portability and efficiency
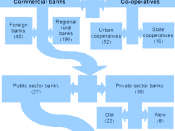
Pakistan has a well-developed banking system, which consists of a wide variety of institutions ranging from a central bank to commercial banks and to specialized agencies to cater for special requirements of specific sectors.
State Bank of Pakistan reins the monetary and credit system in Pakistan. The SBP is performing many useful functions.
Functions like custodian of cash reserve of commercial banks, custodian of foreign currency reserves, bank of rediscount, central clearance, settlement and transfer, and conducting monetary policy for the stability of the entire banking industry of Pakistan.
Quality and Six Sigma is now becoming a part of the culture in the banking sector
about research
aims & objectives
Since recent few years in Pakistan once has witnessed a rapid increase in the number of banks operating in Pakistan. The banking sector has risen to new heights. The local public is more aware of banking procedures and products it used to be ever before. Banks are now offering a wide range of consumer oriented products. There is a shift from corporate banking to consumer side. The most demanding issue in banking sector is regarding their services, win the hearts of the customers & win their money! So the application of Six Sigma plays a vital role in determining the standards followed by different banks.
One of the basic issues faced by any service industry is the quality of service they are providing to their customers. Customers tend to go to banks that have quick response for them. Six Sigma defines the criteria for the industry to follow it and conform according to standards.
Competition in the banking scenario has created both challenges and opportunities for many banks in the field. To succeed, Local banks must come up with good and sound appealing consumer products with no reliability issues. In order to achieve this they have to follow the best quality management approaches. Pakistani banks need to focus on international standards in order to meet the challenges created by the international competition in this sector.
The aims and objectives of this study include:
To have a study on the applications of Six Sigma in Pakistani Banking industry.
To lay down a solid path for the upcoming fleet of researchers, in order to provide them a basis for further studies in the subject area
To fulfill the course requirement of Total Quality Management
limitations of the study
As Six Sigma is an approach to measure progress so due to restrictions of time we will try our best to bring the element of authenticity in our report.
We have chosen the Banking Industry as our targeted Service Sector due to the enormous size of the whole service sector
It might be difficult to get appointments from concerned authorities and financial institutions.
Moreover, as all the group members are currently employed, so it will be difficult to cope up with the project schedule
Hence, we will be limiting our sample size due to cost and time constraints
approaches to the study
possible methods of approach
The possible methods used for completing this research are as follows:
1.Intercept interviews from the concerned executives in order to obtain complete information and actual scenario or picture about the application of Six Sigma in Banking Sector.
2.The next possible alternative is to obtain information from secondary data that is already available.
3.Combination of both the above.
selected approach
1.Secondary data is of great significance and hence we analyze to check the causes or potential problems. These analysis can than be used to design future course of action and hence in policy making. Since the secondary data refers to data collected previously and does not include any modifications implemented presently it cannot be called as a very good tool to deduce present situation.
2.As the people who are associated with organization are better aware of the global environmental changes so it is the most suitable option to interview the executives in order to gain this information which may not have been published as yet. Hence this information can be used to infer plans that are more practical and more realistic.
research methodology
This research is basically applied research and falls in the category of descriptive research.
It falls in the category of descriptive research as we have collected data regarding the topic and made conclusions by analyzing the data and information. Descriptive research relies on qualitative data.
sampling
It is the process of taking (choosing) a sample for the research purpose. There are two types of sampling methods:
(i)Random Sampling
(ii)Non-Random Sampling.
sampling method
The sampling method that has been used is Judgment sampling, which is one of the methods of non-random type of sampling. Hence, we will be exploring different banks who successfully apply the six sigma application by employing this sampling method.
research findings and analysis
Many benefits have been attributed to the application of six sigma. However, the existing body of anecdotal literature on the application of six sigma in banks lacks systematic measurement and multi-organization comparisons.
six sigma as an indicator of quality banking
This survey of the four banks where six sigma was implemented in Karachi examined the extent to which six sigma application was an indicator of quality banking practices. The study concentrated on five quality system elements: defining policies, measurement, analysis, implementation and control.
Based on data from the interviews with these Banking officials, the study found significant variations in the implementation of Six Sigma compliant quality system. The research concluded that Six Sigma application is not an indicator of the strength of a banking service, processes, or its quality system. We would like to add that Six Sigma application is not a guarantee that the certified quality system fulfils all the requirements specified in the standard. Two of the participants in the study reported that their Six Sigma application compliant quality system did not adequately address the five quality system elements examined.
The study also found that Six Sigma application met the expectations of all the respondents. None of the participants in the study reported that opting for Six Sigma application was a failure.
The results of this study indicate that the value of Six Sigma application for banking services was not consistent. The researcher identified the requirement for further research.
banking process improvements through six sigma
One of the objectives of this study was to gain a better understanding of the banking service and process improvements achieved through Six Sigma application.
Based on data from different bank's, discussions with internal and external auditors, and interviews with bankers working in the industry, we as researchers identified key success factors for banking service and process improvement via Six Sigma.
Success factors describe the aspects that the respondents considered to be the most helpful when implementing Six Sigma. The sequence of the following factors surely does not indicate their importance.
*Increased customer delight with problem resolution.
*More precise control over payments to suppliers.
*Increased productivity of new hires via training.
*Elimination of significant travel expenses.
*Enhancement of enterprise e-mail governance to
improve productivity.
*Reduction of credit risk assessment considered
biased.
*Elimination of significant numbers of electronic
information subscriptions.
*Increased associate retention in key areas.
*Increased collections by reducing abandoned
inbound calls.
*Improved ability to detect and prevent fraud at
banking centers.
The list of success factors reveals that banks typically take a more comprehensive approach to achieve banking process improvement than the minimum requirements of the Six Sigma.
The research attributed several benefits to Six Sigma application. Most of the banks reported achieving substantial improvements during the implementation. The development by banks of a clearly defined organizational structure and procedures helped identify and address process weaknesses. Their own formal customer perception surveys provided unbiased and unprejudiced feedback on the quality of banking products and services. Internal quality audits improved job satisfaction and provided an opportunity for staff to discuss the strengths and weaknesses. These benefits and the preparation of guidelines, checklists, templates and tools led to the conclusion that Six Sigma application contributes to improved efficiency, shorter development times and lower costs.
- a quality future !
Given the growing importance of Six Sigma in Banking sector, it's little wonder senior executives and business leaders hiring and promoting leaders on their teams are increasingly looking for candidates who have Six Sigma skills and the ability to apply them practically. The highly competitive environment within our Banking Sector has made training and certification a self-enforcing requirement for career advancement.
Quality and Six Sigma is now becoming a part of the culture in the banking sector, thanks to senior commitment, a robust internal training program, aggressive and ongoing external recruiting and results that excite everyone in the company. They are determined that quality and Six Sigma will help provide the break-through performance to get them on top.
expected benefits compared to actual benefits from six sigma application
On the basis of following factors, we tried to examine the Expected Benefits and their comparison with the Actual Benefits sought by our respondent's firms; the result can be depicted as follows:
FactorRespondents Expecting BenefitsRespondents that Actually Realized Benefits
Market Share22
Better Customer Relationships04
Lower Costs of Poor Quality 31
Increased Staff Motivation40
More Effective Organization31
implementing six sigma in pakistani banking industry
Six Sigma is widely accepted in manufacturing circles as a program that can improve efficiencies and reduce costs. Now Six Sigma is being used by many large financial institutions to improve business processes in financial services - from increasing customer satisfaction to implementing technology.
Technology continues to help banks and other financial institutions decrease costs, boost efficiencies, and improve customer service. Just about everyone in financial services has a "gut feeling" that technology makes customers happier and banks more profitable, but from platform automation systems to check imaging systems to back office accounting systems, it's difficult to quantify the direct impact of technology in financial services.
If you can't quantify the impact of technology, how do you know where to spend your technology budget? Will a new platform automation system enable your tellers to provide faster service and, if it does, do your customers care? Will installing more ATMs improve customer retention by providing additional delivery channels? If you don't know the answers to these types of questions, it's nearly impossible to wisely spend your technology budget. What you end up with is a "hit or miss" approach to selecting technology initiatives, spending money on technology that does not provide the desired results.
Gut feelings may be wrong
Which of the following are true?
1.An experienced teller processes transactions at his or her window more quickly than a less experienced teller.
2.Older customers take more time to complete transactions at the teller window than younger customers.
3.Customers don't mind a longer wait in the teller line as long as the service at the window is friendly.
If one thinks that all of the above are true, he/she might be right, but might also be very wrong. From our research we have found that for most banks, surprisingly, these statements are false, illustrating that some of the most accepted assumptions about customer behavior can turn out to be wrong. The problem is exacerbated when financial institutions install technology in response to perceived assumptions, only to find out that the technology does not provide the intended results. Is the technology to blame? No, of course not!
But how can we be sure that experienced tellers take longer to process transactions than less experienced tellers? By applying the structured principles of Six Sigma, we've been able to determine and measure, with certainty and not guesswork, which factors affect transaction time. While we initially thought that a new teller would take longer to process transactions due to unfamiliarity with the process or needing help from a supervisor, we instead found that, although experienced tellers could perform a transaction more quickly, they spent more time engaging customers in friendly chit chat or cross-selling more products because they were more comfortable in their teller role.
six sigma
Six Sigma is a highly structured program for improving business processes. First used by firms such as Motorola (which owns the Six Sigma trademark for process improvement and boasts $16 billion in cost reductions in 15 years) and GE to eliminate variations or defects in the manufacturing process, Six Sigma identifies the factors leading to variations or defects, and then seeks to eliminate them. Six Sigma is all about measurement: the Greek letter 'sigma' is used in statistics to indicate standard deviation, or to what extent a process deviates from perfection. Six Sigma is defined as 3.4 defects per million products. Today, Six Sigma is a widely accepted program in manufacturing circles that can improve efficiencies, reduce costs, and virtually eliminate product defects.
Let's consider an example of making widgets. The first step in Six Sigma is to identify all the factors that contribute to making widgets. Each factor is then assigned an acceptable range. For example, temperature in the manufacturing facility must be between 68 and 72 degrees to not impact the widget manufacturing equipment. Since temperature variations can result in defective widgets, controlling the temperature variations has a direct effect on product quality.
Now coming to our point, what does Six Sigma have to do with banking and finance, where widgets are replaced by financial products and services? Plenty, of banks and financial institutions are reaping benefits from their Six Sigma applications. Today, Six Sigma is used by some of the largest financial institutions in the U.S. - and it will increasingly be used by banks of all sizes within the next few years.
Any business process -- be it manufacturing or retail or financial services -- can be improved by applying Six Sigma principles. By quantifying the factors that impact how happy a customer is with a product or service and measuring those factors the same way every time, you can then strive to keep those factors consistent and therefore increase customer satisfaction. Rather than rely on anecdotal evidence, you have direct evidence of what needs to be corrected.
how to apply six sigma to banking
Let's apply Six Sigma principles to improving customer satisfaction in bank branches. The first step is to define the factors that result in customer dissatisfaction. Wait times, errors, unfriendly staff, and inaccurate customer information are some of the factors that come to mind.
But all factors are not equal. In our experience, customer wait times typically (although not always) have the most impact on customer satisfaction. You therefore need to determine the activities that affect wait time, such as the number of tellers on duty during any given time of day, tellers having to leave the window to get approvals from supervisors, or ill-prepared customers arriving at the teller window. How you gather the information can vary, from tellers recording their own transaction times and factors, to employing outside consultants to do third-party observations.
Once you determine the factors that affect wait time, you then work to minimize their impact. For instance, if you determine that longer wait times are a direct result of tellers needing to leave the window to get approvals, you then measure the impact of having supervisors grant approvals by going to the teller window themselves, or the impact of eliminating approvals altogether.
In one example, a bank determined that each teller transaction took an average of 2.45 minutes. By identifying the factors that contributed to the transaction time, and controlling them, the bank was able to decrease the average transaction time to 1.80 minutes, significantly improving customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma can be used for much more than reducing teller transaction times. It can be used throughout the organization to enable management to make intelligent decisions about how and where to implement technology. For example, banks have applied Six Sigma to decrease the number of reversals they need to make by identifying the factors impacting reversals, and seeking to eliminate or reduce those factors. Banks have also successfully used Six Sigma to reduce fraud.
Six Sigma is an iterative process. Once you determine the impact of different factors, you continue to monitor the process to make sure that the significance of those factors doesn't change.
The beauty of Six Sigma is that there is no end to the improvements you can make. Once an organization gets a taste of the type of process improvements that Six Sigma enables, they become addicted to a culture of process improvements. Success breeds success, and Six Sigma provides plenty of success.
As mentioned earlier that managers in any industry can improve any business operation by applying Six Sigma's DMAIC process - that is to Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control the key processes that affect customer satisfaction.
define
The first step of the Six Sigma DMAIC initiative is to clearly define the boundaries and objectives of a specific project. For retail banks, improved branch-customer satisfaction is usually a key objective. The first step here is for the bank to define the core processes within the organization that involve customer interactions and are directly related to customer satisfaction. Specific examples might include teller window transactions, new account openings, CD rollovers and address changes.
measure
The second step is for managers to establish quantitative measures that can yield statistically valid data. Not all factors have an equal impact on customer satisfaction. Retail banks generally find that wait times typically have the strongest impact on customer satisfaction. To benchmark performance, the bank may set a key metric of servicing 85% of its retail customers within five minutes. The bank can then assign observers to measure wait times at various branches under differing conditions.
analyze
Once the bank has defined the parameters, documented baseline performance and gathered data, it must then analyze results to identify opportunities for improvement. The analysis must examine all the activities that are part of each bank/customer interaction. Activities involved in check cashing, for instance, may include the customer's preparations before coming to the window, the customer's request for cash back, and the teller's having to seek manager approval for the transaction. The bank must examine each of these activities to determine which have the greatest impact on overall transaction time.
It is important to apply accepted statistical tools to identify the root causes of problems in this business process. Assume that the data gathered shows that customers were unprepared 50% of the time and that manager approvals were required in only 15% of all check-cashing transactions. Lack of customer preparedness might appear to be the greater contributor to longer transaction times. Proper regression analysis, however, may reveal that managerial approvals -- which usually require that tellers leave their windows -- have a much greater impact, adding more than five minutes to actual wait times.
improve
As soon as the bank identifies the factors that slow transactions, it should initiate actions to minimize the impact of these factors. The bank can, for example, design experiments to evaluate the impact of proposed improvements to every activity in the check-cashing process. To eliminate the need for tellers to leave the window for manager approvals, the bank may set up an experiment where supervisors come to the teller window. In a separate experiment, the bank may measure the impact of letting tellers approve more transactions on their own. Careful measurement of wait times in these two experiments will indicate which new practice has the more beneficial effect on wait times.
control
Control is the final step in the DMAIC cycle. The control step demands that the bank continually monitor the metrics it has put into place. This process requires periodic measurements using the same data-gathering protocols established at the beginning of the project.
Perhaps the greatest strength of the Six Sigma method is that it produces objective, measurable results that can be monitored continuously. In one case, a bank implemented a Six Sigma project to reduce customer wait times, just like in our example. By identifying and controlling the key factors that did the most to increase transaction times, the bank was able to lower its average transaction time from 2.45 minutes to 1.80 minutes, significantly improving customer satisfaction while simultaneously reducing staffing costs.
But Six Sigma principles are not limited to reducing customer wait times. Banks have also implemented Six Sigma programs to reduce theft and fraud, and to meet other objectives as well. The Six Sigma DMAIC process can be applied throughout the banking organization, wherever managers require measurable results, to design, validate and monitor business process improvements.
Applying Six Sigma's DMAIC process has enabled banks to implement corrective actions based on empirical evidence rather than on anecdotal evidence and gut feeling. In addition, a successful Six Sigma project establishes a precedent for evaluating new programs and technology investments.
In most of the bank's CIO's face constant demands from senior management to document "results" for IT expenditures. Six Sigma offers a proven methodology for establishing such results. More important, the quantitative results that Six Sigma provides will allow CIO's to propose and test continued improvements, both to their own IT operations and to the mission-critical business processes they support.
conclusions drawn
Only six sigma application is not a true indicator of product or process quality
All participants reported that six sigma had at least partially met their expectations
To achieve substantial banking process improvement, it is necessary to implement a more comprehensive approach to six sigma application than simply satisfying its requirements
Greater benefits from six sigma application were realized by banks who were lacking established processes, explicit organizational structures, and standards and procedures
Six Sigma Application helped save time, money and effort
The six sigma group placed more importance on design reviews and code inspections, project planning and the involvement of managers from all levels in the planning process.
Achievement of corporate objectives and improvements to market share were the main reasons for six sigma application
Improvements are expected in providing service, product quality, communication, process design, public image and sales relations
The most demanding six sigma requirements are: defining, measuring, analyzing, implementing and controlling
None of the respondents identified a lack of management commitment as a significant barrier to six sigma
Six Sigma application contributed to improvements in operating efficiency, customer satisfaction, competitive position, time required to train new employees
The main barriers to six sigma application were the cost of implementation and the documentation requirements
Customer Retention was the main reason for pursuing six sigma application
Organizations that achieved the least benefit from application of six sigma undertook the initiative to address customer demand and to increase their market share
Organizations that achieved the most benefit from application of six sigma undertook the initiative to improve efficiency, customer service and reliability
appendices
six sigma - what is six sigma?
Six Sigma in many organizations simply means a measure of quality that strives for near perfection. Six Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects (driving towards six standard deviations between the mean and the nearest specification limit) in any process -- from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service.
The statistical representation of Six Sigma describes quantitatively how a process is performing. To achieve Six Sigma, a process must not produce more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. A Six Sigma defect is defined as anything outside of customer specifications. A Six Sigma opportunity is then the total quantity of chances for a defect. Process sigma can easily be calculated using a Six Sigma calculator.
The fundamental objective of the Six Sigma methodology is the implementation of a measurement-based strategy that focuses on process improvement and variation reduction through the application of Six Sigma improvement projects. This is accomplished through the use of two Six Sigma sub-methodologies: DMAIC and DMADV. The Six Sigma DMAIC processes (define measure, analyze, improve, control) is an improvement system for existing processes falling below specification and looking for incremental improvement. The Six Sigma DMADV process (define, measure, analyze, design, verify) is an improvement system used to develop new processes or products at Six Sigma quality levels. It can also be employed if a current process requires more than just incremental improvement. Both Six Sigma processes are executed by Six Sigma Green Belts and Six Sigma Black Belts, and are overseen by Six Sigma Master Black Belts.
According to the Six Sigma Academy, Black Belts save companies approximately $230,000 per project and can complete four to 6 projects per year. General Electric, one of the most successful companies implementing Six Sigma, has estimated benefits on the order of $10 billion during the first five years of implementation. GE first began Six Sigma in 1995 after Motorola and Allied Signal blazed the Six Sigma trail. Since then, thousands of companies around the world have discovered the far reaching benefits of Six Sigma.
Senior Leadership is responsible for the strategic plan, and selecting potential six sigma plus project areas. Once a six sigma plus project is understood using total quality management (tqm) tools, total quality management (tqm) techniques generate alternatives. Improvements are then implemented. Six sigma plus projects maintain improvements using control tools of total quality management (tqm). This is the define, measure, analyze, improve and control sequence (DMAIC) of six sigma.
why should banks implement Six Sigma?
'SIX SIGMA -- IT'S NOT JUST FOR MANUFACTURERS ANYMORE'
During the past 10 years, businesses have deployed a wealth of information technologies to increase revenue, reduce operational costs, and improve customer service. Yet many CEOs find it difficult to tell whether these investments are producing satisfactory ROI. To understand what really works, and why, these enterprises are turning to process-improvement methodologies like Six Sigma.
Developed in the 1980s by Motorola Inc. to reduce manufacturing defects, the Six Sigma methodology focuses on eliminating the defects that drive customer dissatisfaction and customer defections. (Indeed, some observers have characterized Six Sigma as a "defect-reduction" methodology.) Users of the Six Sigma methodology have demonstrated that the surest way to improve performance is to systematically identify the causes of waste, lost productivity and customer dissatisfaction, and then adjust internal processes to eliminate them. These successes have encouraged many retail and service businesses to apply Six Sigma to non-manufacturing operations.
The Six Sigma methodology demands that a company begin by identifying the defects that influence customer satisfaction the most. For each factor, the company then determines an acceptable range.
how does the six sigma work?
Managers in any industry can improve any business operation especially banking operations by applying Six Sigma's DMAIC process -- to Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control the key processes that affect customer satisfaction. Since we are involved in applying six sigma in banking sector, we will use an example from retail banking.
During the past 10 years, retail banks have implemented numerous new technologies and marketing programs to improve service delivery and boost earnings. Banks offer an ever-widening range of financial products through constantly expanding branch networks. To successfully market new products like investments and insurance, banks now find themselves cross-training branch employees for a much wider variety of roles. For a bank to make sure it has the right people with the right skills available at the right time is a growing challenge.
Optimizing staff levels is only one example of the challenges that retail banks face as they struggle to improve branch-customer satisfaction while simultaneously reducing costs. Today's customers demand a positive service experience -- accurate, friendly and fast -- every time. If they don't get it, they won't hesitate to defect to a nearby competitor.
six sigma and the banking industry
In todays fast paced and fierce competition nearly each and every bank has set a goal to be the premier international financial company in this millennium. To achieve this clearly ambitious goal, these banks have to implement quality initiatives that satisfy customers quickly and flawlessly at every interaction anywhere in the world. Six Sigma quality was always in the domain of the manufacturing arena--the question was could it work in the service industry? Could it work worldwide for a financial organization? Or to be much straight could it work for a Bank?
Banks undertook this challenge to improve total customer satisfaction by investigating well-known manufacturing management theories and attempted to apply them to their own nonmanufacturing environment. Methodologies like cycle time reduction (CTR), coupled with the detection of defects using Six Sigma methods and implemented globally by using empowered teams, have resulted in significant improvements in process timelines, cash management and customer loyalty and satisfaction.
cycle time reduction
Most people think reducing cycle time applies only in the manufacturing sector, but banks found CTR to be extremely useful in financial areas, such as consumer banking and emerging markets.
To achieve CTR, first of all the cross-functional process mapping (CFPM) methodology must be developed. CFPM involves developing "maps" of process flows by describing the functions involved in each step of a particular process. Maps are developed for both the way things are being done (called the "as is" map) and the ways things should be handled (the "should be" map).
In the beginning, banks established the Cross-Functional Performance Challenge within its divisions by using the Six Sigma methodology to identify defects, CFPM to map the steps for improvement and empowered teams to correct the defects.
At its core, CFPM involves eliminating wasteful steps, which are defined as any activities that don't contribute to the goal of meeting customers' needs.
relocating, retraining and regaining
There are cases when a bank needs to be relocated for any reason. In such scenarios some banks face serious problems when back- office operations relocate from one city to another. The department goes through a transition period, and when that period is completed, there are some people who chose not to relocate. So it is left in the hands of the new people who are basically inexperienced in the job they are handling. When problems come up, neither they nor their supervisors know how to fix them.
To address such issues problem, many banks implemented the Asset-Based Finance Cross-Functional Performance Challenge. A crucial part of the Asset-Based Finance team's progress was vesting the authority to "sign off" on loan availment to his team. By reducing the number of "hand-offs" necessary to make funds available, the cycle time for this segment of the availment process was reduced by an average of 75 percent, from two hours to 30 minutes.
After the completion of the project, banks proved that it was very successful with reduced cycle time. Instead of getting complaints from customers, they were thus getting compliments.
identifying defects using six sigma
Customers who do business banks sometimes initiate manual funds transfers. When they want to send money from their accounts, they call their banker and then fax, phone or mail in requests to have the transaction processed. Because the process was so complicated, customers complained. Most of the complaints lodged with the department dealt with the time it took to complete the process, from "I can't understand why you don't have my request," to "When will my transaction be confirmed?"
If the request wasn't the banker's top priority for the day, it would sit there for two or three hours before it even went to the back office.
Once the bank employees had identified the primary obstacles preventing them from achieving total customer satisfaction, they were able to correct the problems with the Six Sigma program.
A sigma is a statistical term that measures to what extent a process deviates from perfection. Three sigma equals 66,807 defects per million opportunities; six sigma equals 3.4 defects per million opportunities--virtual perfection. The goal of the banking sector is to reduce in defects and cycle time by 10 times by December 2006 and reduce defects and cycle time by 10 times every two years thereafter. Wow!
Six Sigma is achieved by using simple tools such as the Pareto chart. The data on the chart identifies which problems occur most often or incur the highest cost. It provides direct evidence of what should be corrected first. Vilfredo Pareto, the Italian economist for whom the chart is named, theorized that 20 percent of possible causes are responsible for 80 percent of any problem.
A team composed of bankers and operations people identified the entire funds transfer process, tabulating defects and analyzing them using a Pareto chart. High on the chart of defects was the internal call-back procedure, which required staff to call the person requesting the funds transfer to make sure that the instructions were correct and hadn't been altered.
In this manner the banks were able to cut monthly call backs from 8,000 to 1,000 on an average, and eliminated call backs for 73 percent of the transactions coming in.
In another example, Six Sigma methodology can be used to help track defects and document the results by teaching team members to identify appropriate metrics, determine a baseline, establish appropriate standards and monitor execution. These solutions required employees to form teams to solve the issues discovered.
To reduce the time for opening an account, banks must form a cross-functional global team of 80 people. The team first identified sponsors and formed a steering committee to champion the effort. Employees must be invited to participate based on their subject matter expertise and ability to assist with the solution. The largest obstacle is enabling them to find time to participate while juggling daily job responsibilities. Consultants can help to define the management system around which the team will be organized.
Team members work well together, because achieving the objectives would make their professional responsibilities easier and would benefit their customers--a win-win situation for everyone.
The focus on cycle time and defects has made an impact on how a bank serves customers. It's not just a matter of doing things faster; it's doing things better. This means no redundancy, minimal hand-offs and metrics that reflect performance in the eyes of the customer.
Introducing quality as a core strategy can be viewed as a unique opportunity and differentiating feature not only vis-Ã -vis the customers, but also the banks staff. When six sigma will be implemented correctly, quality will increase customer satisfaction and will thus lead to shorter reaction time and faster introduction of new products--providing a sustainable competitive advantage.
working together
The first step in process mapping is establishing a team, typically of 30 to 50 people, drawn from every unit that contributes to the process. Cross-functional teams, made up of representatives from each functional department, develop maps. They include employees deep within the company--the "doers" of the current process. Because of their close vantage point, these employees can offer valuable insight into daily business operations. Management empowers the team to implement any changes they develop that will reduce the cycle time and improve customer satisfaction.
CFPM has five phases. First there's planning, when the critical business processes to be mapped are identified and a team is selected. Next, the team meets for four to five days to map all current steps and identify what is not working now--the "as is" process.
The team then takes the map back to colleagues throughout the organization to verify its accuracy and to see if there are any more problems or issues they want to add; this helps secure buy-in for simplifying the process. The 'as is' mapping session is a very critical step in the process. Until one map those processes out, one cant find out where the problems are. This step enables to design a streamlined 'should be' process map.
After completing the "as is" map, the team meets again to map out the desired, streamlined process, the "should be," which has removed nonvalue-added steps. The last phase, which is probably the most difficult and can take several months, is the implementation of the action items to achieve the "should be" process. Even after the process has been improved, CFPM doesn't end.
people helping people
For CFPM to work there must be a commitment at all levels, with everyone taking leadership roles. In fact, key team members must spend one-fourth of their time on the project. Team leaders must spend at least three-fourths of their time for up to a year. When these teams will be challenged to reduce cycle times within their departments, they will become empowered to make improvements, which will thus lead to improve the corporate culture.
The staff members know what is wrong with their piece of the process. By bringing them together, we will be able to understand what's wrong with the process end-to-end, design an improved process and give them time to implement it. The tools help the team stay focused and understand the root cause of the problem.
amazing results waiting ...
Using process mapping, Motorola has driven down manufacturing time for pagers from 40 days to less than one hour. This kind of improvement is an indication of why banks chose Motorola's mapping process, and what a quality culture can accomplish--how cycle times can radically be reduced by a factor of 10 every two years.
"Motorola has done a particularly good job of assessing its competitive position, and has become pretty well-known in the industry for reducing cycle time," asserts one of the heads of a leading bank.
CTR has met the challenges of many banking groups, including the following:
*Private Bank--Western Hemisphere, which serves wealthy individuals. This group reduced internal call backs by 80 percent, external call backs by 85 percent and the credit process time by 50 percent.
*Global Equipment Finance, which provides global financing and leasing services to Citibank customers. This group improved all steps' cycle times from when a customer places an order to product delivery. The group also reduced the credit decision cycle by 67 percent, from three days to one day.
*Copeland Companies, subsidiaries of Travelers Life & Annuity, which are distributors and record keepers of financial service products, primarily through defined contributions such as 401(k) plans. This division used CFPM methods to improve the accuracy and timeliness of statements. The group achieved 100-percent accuracy within a four-month period. It also reduced the cycle time of processing statements from 28 days to 15 days.
commitment is needed from the top
Teams involved in the Quality Challenge needed to have full autonomy to make decisions about changes to the process. To champion the work, senior managers must sponsor the quality initiatives or serve on steering committees and keep an "open door" policy so that teams can gain access to them as needed. As far as we have done research we have found out that the involvement of senior sponsors is a continuous process all the way from setting critical business issues and objectives to making the final presentation.
There must be a well-balanced split between projects initiated by senior management and those initiated by staff. The senior country operations officer and corporate bank heads must be the most active supporters of our CFPM projects. Their commitment helps balance back- and front-office aspects of the projects.
the big picture
The goal of becoming the premier international financial company in this millennium by most of the banks will require a devotion to excellence on the part of every employee. The goal is ambitious, but banks need to implement quality initiatives to make certain that it satisfies customers flawlessly and quickly at the point of every interaction anywhere around the world. By making innovative use of information technology and operations management through Six Sigma and CFPM, employees will work faster and will create high levels of customer satisfaction.
banking industry of pakistan:
performances & constrains
"The banking industry should determine where improvement is needed, how service can be improved and where operating system breakdowns occur, why they occur and how they can be avoided."
Banking is one of the most sensitive businesses all over the world. Banks play very important role in the economy of a country and Pakistan is no exemption. Banks are custodian to the assets of the general masses. The banking sector plays a significant role in a contemporary world of money and economy. It influences and facilitates many different but integrated economic activities like resources mobilization, poverty elimination, production and distribution of public finance. It is purchase of car or building of home banks is always there to serve you better. It is play ground or any educational or healthy societal activities the money of banks nurtures them. It is an industrial project or agricultural development of the country the sponsor-ship of banks is very much involved. Banks play very positive and important role in the overall economic development of the country.
Pakistan has a well-developed banking system, which consists of a wide variety of institutions ranging from a central bank to commercial banks and to specialized agencies to cater for special requirements of specific sectors. The country started without any worthwhile banking network in 1947 but witnessed phenomenal growth in the first two decades. By 1970, it had acquired a flourishing banking sector.
state bank of paksitan: linchpin of country's banking system
SBP acts as a nucleolus in the financial system of the country. It is the linchpin of country's banking system. Today, a central bank is the central arch of the monetary and fiscal framework in many countries of the world and its activities are essential for the proper functioning of the economy and critical for the fiscal operations of the government and Pakistan's banking system is no exemption. State Bank of Pakistan was established on the first of July 1948 under the SBP order 1948 as the central bank of the country.
The present structure, operation and authority of the SBP originate from the SBP Act 1956. State Bank of Pakistan is entrusted with the prosperity, stability, and growth of the domestic economy. It is sole bank of issue, holder of gold and currency reserves, banker to the government, lender of the last resort to commercial banks and supervisor of the others banks. It is also responsible for National Credit Policy.
In October 1993, complete autonomy was granted to SBP. It was the milestone in the history of SBP. Main reason of its full autonomy is to assume increased independent inputs in macro economic policy making of the country. Autonomy granted to the SBP has strengthened its supervisory and regulatory powers. With the abolition of Banking Council, the multiplicity of regulatory authorities has been removed and SBP has become the sole regulatory authority for the purpose. Now all financial institutions have also been under the supervision of SBP. The SBP also enjoys extensive powers of qualitative credit control.
State Bank of Pakistan reins the monetary and credit system in Pakistan. The SBP is performing many useful functions like custodian of cash reserve of commercial banks, custodian of foreign currency reserves, bank of rediscount, central clearance, settlement and transfer, and conducting monetary policy for the stability of the entire banking industry of Pakistan.
comparative study of domestic banking industry
Nationalization of banks in the seventies was a major upset to domestic banking industry of the country, which changed the whole complexion of the banking industry. With irrational decision at the top all the commercial banks were made subservient to the political leadership and the bureaucracy. Specialized banking institutions were already working in the public sector. The new accountability paradigm changed the business ethics in the banking industry, and with this change started the disaster. Nationalization of banking industry was accompanied by violent changes in the external value of rupee. The commercial banks thus lost their assets management equilibrium, initiative and growth momentum. They ceased to be a business concern and became big bureaucracies. This was accompanied by indiscreet loaning under political pressure. They suffered from three terminal diseases: non-performing loans; higher intermediation cost; and loss of initiative and entrepreneurship. The rise to Labour Unions and Officers Associations made life tough and working conditions ugly to honest, dedicated and industrious workers in the realms of domestic banking industry.
The era of nineties was the climax of privatization, deregulation and restructuring in the domestic banking industry and financial institutions. The Muslim Commercial Bank was the first bank to privatize. Followed by Allied Bank limited, United Bank Limited and now the Habib Bank Limited have been privatized. One thing good for that particular period was the recruitment of fresh officers in the domestic banking industry through well-organized policies of Banking Council. With the decay of Banking Council there was flood of insincere, nonprofessional, incompetent candidates directly appointed/ recruited in all the domestic banks of the country.
Statistics
public sector commercial banks
National Bank of PakistanNBP
First Women Bank LimitedFWB
The Bank of KhyberKB
The Bank of PunjabBOP
The government of Pakistan permitted small private sector banks to operate, which indulged in doubtful policies to promote business. The public sector banking, which constituted the backbone, thus continued to suffer because of their approach, size and carried over liabilities. Mehran Bank is the prime example of that kind of lax banking in the country, which ultimately merged into National bank of Pakistan i.e. last resort of domestic banking industry.
local private banks
Muslim Commercial Bank Limited
Askari Commercial Bank Limited
PICIC Commercial Bank Limited
Saudi Pak Commercial Bank Ltd
Prime Commercial Bank Limited
Platinum Commercial Bank Ltd
Metropolitan Bank Limited
Allied Bank of Pakistan
Bank Al Habib Limited
Bank Al-Falah Limited
United Bank Limited
Faysal Bank Limited
Soneri Bank Limited
Union Bank Limited
MyBank Limited
Mashreq Bank
In the meanwhile, western banks started entering into the business. They, with the support of ruling elite, concentrated on the big business, leaving the routine business to the local banks. This reduced the profitability of the local banks.
foreign banks
Hong Kong Shanghai Banking Corporation
The Bank of Tokyo Mitsubishi
Credit Agricole Indo Suez
Standard Chartered Bank
Habib Bank A. G. Zurich
Al Baraka Islamic Bank
Mashreq Bank PJSC
Dubai Islamic Bank
Rupali Bank
Oman Bank
Doha Bank
CITI Bank
specialized banks
Punjab Provincial Cooperative Bank Limited
Industrial Development Bank of Pakistan
Zari Tarqiati Bank Ltd.
problems of domestic banking industry of pakistan
a) knowledge of risk management is missing
The main purpose of financial and banking organization is to create valuable system by interacting with its environment, customers, constituents, suppliers, technology, competition, economy, government, etc. A valuable system is created by the conversion of available resources i.e. human, financial, physical, and intangible assets into goods and services that fulfill the needs of the customers and save the best interests of the banking and financial organization. Risk management performs all these diversified but integrated work to achieve maximum out-put. Managing risk is actually managing the organization: planning, organizing, directing, and controlling organization systems and resources to achieve objectives. Managing risk must come from within and act to change the organization and its response to changes in the environment.
Now many domestic banks are hiring experts of risk management to secure their precious assets. National Bank of Pakistan has also created risk management group at head office and as well as regional level to save the best interests of the bank and enhance the chances of investments.
b) total quality management: paradigm shift
Ours is the age of cutthroat competition, scarcity of resources, technological advancement, integration of financial services, expansion of economic markets and cultural diversity. In these complicated and conflicting financial and economic scenarios the need of TQM in the ranks of domestic banking industry is indispensable. The middle management should need to have basic understandings about complicated management processes, crisis management tools, marketing/product strategies, financial and treasury management techniques, financial discipline, soundness and transparency of banking system, human resource administration and above all genuine leadership qualities to adequately operate within a highly sensitive and complicated industry.
There is urgent need of having TQM in the realms of banking industry of the country. At the dawn of WTO and increasing chances of investment banking among the SARRC countries the TQM is the need of the hour, Our commercial banks must pay attention to this shift and start thinking strategically for providing high quality products and services to customers. According to a study from Business Communications Company, Inc. The Changing Global Commercial Banking Industry Structure, total commercial banking assets are expected to climb at an average annual growth rate [AAGR] of 7.1% from $6,772 billion in 2001 to $9,537 billion in 2006.
The banking industry should determine where improvement is needed, how service can be improved and where operating system breakdowns occur, why they occur and how they can be avoided.
areas where improvements is to be needed
*Internal & External Audits (concept of financial discipline, accountability, good corporate governance, professionalism and impartiality)
*Communications Skills. No ambiguity should be left. Clear and comprehensive instructions
*Transparency in all matters especially in financing
*Aggressive marketing strategies in retail and commercial banking
*Institutionalization of Human Resource Management (best man should be posted to best assignment, refreshing courses, seminar on emerging banking and financial problems etc. etc.).
*Humanistic administration, because human is supreme than any entity.(promotion policies, award & reward) etc. etc.
*Research and Development facilities (Domestic market research, economic analysis, strategic insight of major economic and financial accords, international markets knowledge, rigorous planning and development, loss & prevention mechanism)
*There should be central compliant cell in every bank in the country in order to reduce people's complaints and foster the ratios of productivity.
*Commonness of E-commerce and Internet bank should allow flourishing in the domestic banking industry of the country.
*Scope of Investment Banking is very much there and bright as said by finance minister of the country. Concrete efforts should be made to initiate investment-banking operations in the region.
*Money laundering and white-collar crimes are on the rampant. Aggressive and comprehensive mechanism should be set-up to save the domestic banking industry of the country.
*General working conditions ought to be improved
visited bank's
Although the research team planned that we will be visiting 6 to 7 local and multi-national banks, but due to immense pressure of job and work schedule on the team members, we managed to visit just 4 banks out of the planned.
Following is the list of banks we were able to visit along with the key contacts with whom we interviewed. Respective Postal Addresses, Emails, and Web-URLs are also mentioned hereunder:
interview schedule
The following questions were developed in order to facilitate the interviewer at the time of interviewing the respective respondents. Although the interviews were conducted in an informal manner leaving more room for the interviewers to drill down more information from the respondents by asking interlinked questions. Hence, all the questions were designed open ended as the intent was to collect qualitative data!
What do think of Six Sigma as an Indicator of the overall Quality Banking?
What will be your comments about the Business Process Improvements that your bank realized through implementing Six Sigma?
How do you conceive the implementation of Six Sigma with reference to the Costs and Benefits associated with it?
What are the core reason(s) that your bank sought to implement six sigma? What Results did you realized?
What common problems did your bank faced during the whole process of implementing six sigma?
Vis-Ã -vis the following factors, what benefits you are expecting as compared to Actual Benefits realized from Six Sigma?
Market Share
Better Customer Relationships
Lower Costs of Poor Quality
Increased Staff Motivation
More Effective Organization
Biblography
*www.askjeeves.com
*www.SBP.com
*www.quality.com
*SBP libraray


Good One
It is really a good essay with accurate and latest information about banking sector of Pakistan. very suitable for Finance students belonging to Pakistan..
0 out of 0 people found this comment useful.