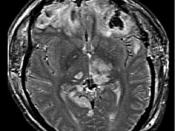
Injury to the head is one of the leading causes of disability in the industrialized nations and a significant cause of death and disability among children and adolescents in the United States. Martin (1988) estimated that each year, 1 million children experience sustained closed-head injuries. A plethora of research on TBI has escalated in an attempt to understand the full ramifications of cerebral insult. Depth and duration of consciousness and age at the time of injury are factors in neurodiagnostic and neuroprognostic decisions regarding recovery and ultimate outcomes of head injury (Martin, 1988). Age of onset, for example, can significantly alter the course of growth, and qualitative differences can be found not only between children and adults but between adolescent and preadolescent youth with TBI. (DiScala, Gans & Grant, 1991)Although technological advancements have provided new information about brain structure and function with adult samples, the absence of demonstrable changes is common on CT scans of children with head injury (Conners, 1973; Dalby & Obrzut, 1991) .
However, the lack of such evidence should not lead to the assumption that there is no brain damage, because behavioral differences and cognitive changes in postmorbid functioning have been documented in cognitive and neuropsychological assessments of children with TBI. (Dennis & Barnes, 1990; DePaepe & Lange, 1994)From a less structural point of view, TBI has been found to be associated with a variety of neuropsychological outcomes in children, including poor performance on speeded tasks, memory impairment, decreased recall, and difficulties in processing novel or complex visual-spatial stimuli. More recently, 5- to 16-year-old patients have been found to display inadequate perceptual processing , with specific impairment of visual memory. A strong relationship was found among declines in adaptive functioning, measures of intelligence, motor and language abilities, and the extent of severity of head injury...