Ulcerative Colitis
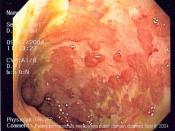
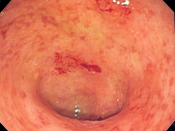
Ulcerative colitis is a type of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) in which the lining of the colon becomes inflamed and develops ulcers. It's believed to be an abnormal response by the immune system. Normally the immune system only responds to harmful bacteria in the body but in ulcerative colitis the immune systems mistakes food and beneficial bacteria in the colon as a threat. This causes the immune system to send white blood cells to the colon thus causing constant inflammation and ulceration.
Ulcerative colitis should not be confused with Crohn's disease. Though both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are both Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, ulcerative colitis only affects the colon where Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Also, ulcerative colitis only affects the lining of the colon but Crohn's disease can affect all the layers of the bowel walls. It is important to not confuse either disease with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), which is a disorder that affects the muscles of the colon.
This disorder isn't prone to intestinal inflammation, which is one of the main indicators of ulcerative colitis.
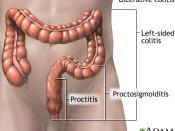
There are four different kinds of ulcerative colitis. They are classified according to location. Proctitis involves only the anus and the rectum. Proctosigmoiditis is the inflammation of the rectum and the sigmoid colon. Left-sided colitis is the inflammation of the entire left side of the colon; the rectum, sigmoid colon and the descending colon. Pan colitis is the inflammation of the entire colon and is the most severe form of ulcerative colitis.
The symptoms for ulcerative colitis may occur suddenly or slowly develop. They vary in severity and time between occurrences. The majority of people affected with ulcerative colitis have mild symptoms. A smaller amount of those affected have very severe attacks...