Understanding Group Interaction and Development
Groups are not formed overnight. They are developed over an undetermined course of time. There is no specific time line, and specification of one would be virtually imposable. However, development of a group can be better understood upon group-specific evaluations. Determination of size, frequency of interaction and structural features directly impact developmental stages. Organizations are built upon structured groups of interdependent people, focused on accomplishing a common goal or mission. (Engleberg & Wynn, 2003) Groups are formed, and can be found, both personally as well as professionally. Understanding these groups and the dynamics which are found within them can be identified through a variance of theories. Such theories form building blocks for group interaction and development.
In 1965 Tuckman derived that there were four critical stages to the sequence of group development; forming, storming, norming and performing.
(Tuckman,1965)
Forming: Is the introduction of new team members.
Though at first all members are uncertain, more aggressive members soon assume group leadership roles, and facilitate group clarity.
Storming: This can be seen as a sort of group adolescence stage. Leadership roles are tested, determined and possibly re-determined. This stage also allows for all members to settle into their appropriate roles within the group.
Norming: In this stage groups explore ground rules, appropriate boundaries, expectations, limitations and goals. This stage is much like "testing the water" within the group, leadership and other group roles are tested. If instability persists within the group, this stage can easily transform back into the storming stage.
Performing: Once stability within the group is formed, members are then ready to address issues at hand, and develop critical problem solving strategies.
(Tuckman, 1965)
Tuckman's developmental model represents the necessary stages, which are found within all groups. Within an organization, when forming groups, these stages...


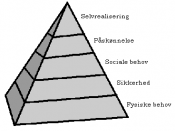
A few questions
What (if any specific types) of groups are you referring to? And then, who are you writing this to? From a business perspective its great, but it seems a little sterile.
2 out of 2 people found this comment useful.