RAID
This paper is going to provide a brief description of RAID and discuss various aspects of RAID. This will include the various levels of RAID, Hardware RAID, Software RAID, and the advantages and disadvantages associated with utilizing RAID.
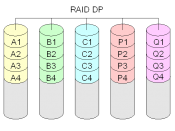
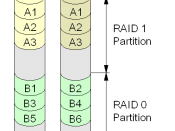
RAID is an acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. The basic idea behind RAID is to combine multiple small, inexpensive disk drives into an array to accomplish performance or redundancy goals not attainable with one large and expensive drive. The underlying concept of RAID is that data may be distributed across each drive in the array in a consistent manner. To do this, the data must first be broken into consistently sized chunks, often 32K or 64K in size, although different sizes can be used. Each chunk is then written to a hard drive in RAID according to the RAID level used. When the data is to be read, the process is reversed, giving the illusion that multiple drives are actually one large drive.
The main benefits in which RAID will provide are data protection and availability. RAID protects your data in the unlikely event of a drive failure. If a disk drive fails in a RAID system, network clients are unaware of the incident and they continue on with their work as if nothing happened. The RAID system continues to perform read/write operations and if a hot spare is available then it automatically becomes part of the array and data that was on the failed drive is automatically regenerated onto this new drive in the array. The various levels of RAID architectures as described by Charles M. Kozierok are defined below.
RAID Level 0 is a misnomer because the storage is not redundant, but it is an array. In RAID-0, data is interleaved across drives for higher data throughput.