Wide Area Networks
Introduction
The following paper is a report into the characteristics and construction of a Wide Area Network (WAN). It will start by giving a basic description of a Wide Area Network and then go on to investigate, in detail, the actual structure and workings of a WAN. The intended purpose of the report is to allow individuals with or without prior knowledge of the researched area to have better understanding of the report subject.
Basic Concepts
Characteristics of a WAN
The term WAN (Wide Area Network) refers to a network, which covers a large geographical area, and use communications circuits to connect the intermediate nodes. WAN's are used across a city, country or even around the globe. Typical transmission rates are 2 Mbps, 34 Mbps, 45 Mbps, 155 Mbps, and 625 Mbps but can be even more than this. A WAN consists, basically, of two or more LANs (Local Area Network), which are connected to each other using WAN technologies under a high-speed communication.
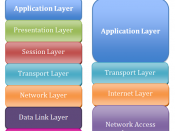
The largest and probably the best example of a Wide Area Network is the Internet. WAN technologies generally function at the lower three layers of the OSI Model: the Physical Layer, the Data Link Layer, and the Network Layer (all layers are shown in order below). . Bridges, routers and multiplexers and other devices are used for correct data transmission. Some WANs are extremely widespread (global), but most do not provide true global coverage. Organizations supporting WANs using the Internet Protocol are known as Network Service Providers (NSP's). These form the core of the Internet.
The OSI (Open System Interconnection) Model: -
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data Link
Physical
Addressing and routing
On a Wide Area Network, the routing of data is done mainly using TCP/IP (Transmission Control protocol/Internet Protocol).
TCP is the protocol, which "enables two hosts to establish a connection and exchange streams of data. TCP guarantees delivery of data and also guarantees that packets will be delivered in the same order in which they were sent."
Every device on a network, or indeed any device in general, has it's own individual IP Address. An IP Address is a unique number in the format of four sets of digits, each ranging from 0 to 255, for example 195.194.202.70. Hardware used to assist the correct routing and flow of network traffic would consist of devices like Hubs, Bridges, Routers, Switches and Multiplexers.
Congestion Control
This is a technique(s) used to detect if there is any other traffic on the network before data is sent. Devices that are communicating data across a network rely on congestion control to determine when to send or delay the transmission of data packets in order to stop contention and collisions. The main technology used for doing this is CSMA/CD Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision. If a collision is detected then the sending device will wait for a certain length of time and then attempts to re-send the message.
PTO switched services
Circuit switched - Circuit-switched is a type of network in which a physical path is obtained for a single connection between two end-points in the network for the duration of the connection such as an ordinary telephone service. This is made possible by the telephone service dedicating a specific physical path to the number that you have called for the duration of your call and during this time, no one else can use the physical lines. Some examples of Circuit Switching techniques are shown here:
PSDN - Packet Switched Data Network
PSDN is a type of Network used in public telephone networks. Data is transformed into packets of a fixed length, which are fixed with the destination and source addresses. The packets are then transported across the network using routers, which read the addresses.
ISDN - Integrated Services Digital Network
ISDN is another international standard used for sending data including voice and video over telephone or digital lines. The two types of ISDN are:
÷Primary Rate Interface (PRI) - Made up of two 64-Kbps B-channels and one D-channel for transmitting control information.
÷Basic Rate Interface (BRI) - Made up of Primary Rate Interface (PRI) -- consists of 23 B-channels and one D-channel (U.S.) or 30 B-channels and one D-channel (Europe).
Leased Lines
A Leased Line is a high-speed, dedicated Internet connection which is rented (leased) from a telecommunications provider i.e. NTL, BT, etc. The speed of the connection can be chosen and upgraded as required to suit the needs of your business. A leased line will also allow the client to run their own email and web servers without the added cost of an ISP. Some advantages and disadvantages of leased lines are shown here: -
Leased line advantages
ÃÂUpload and download speeds are the same.
ÃÂChoice of bandwidths.
ÃÂReadily available SLAs.
ÃÂGuaranteed bandwidth for critical business usage.
ÃÂSuitable for web hosting.
Leased line disadvantages
ÃÂRelatively expensive to install and rent.
ÃÂNot suitable for single or home workers.
Packet switched
Packet switching is when data to be transferred exceeding a networks maximum length is broken up into shorter units, known as packets; the packets, each with an associated header, are then transmitted individually through the network. "The fundamental difference in packet communication is that the data is formed into packets with a pre-defined header format (i.e. PCI), and well-known "idle" patterns which are used to occupy the link when there is no data to be communicated"
Some of the more commonly used packet switching methods are detailed below.
X.25
X.25 technology is connection orientated and will allow computers on different public networks to communicate through an intermediary computer specifically at the Network Layer of the OSI. It is a packet switched device that is used to exchange data between the DCE (Data Circuit Equipment) and the DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) in Public Switched Telephone Network. The protocols used by X.25 operate in close relation to the Data Link and Physical Layer protocols defined in the OSI Model.
Frame Relay
Frame relay operates at the Data Link Layer of the OSI Model. One way to look upon Frame Relay is that it was originally developed as a "poor man's" version of the X.25 technology. It is often sold by Telecommunications companies to businesses looking for a cheaper alternative than leased lines. Frame Relay is being displaced by ATM and native IP based products, including IP virtual private networks. It uses no error correcting mechanisms, meaning that it is capable of transmitting Layer 2 information more rapidly than other WAN protocols.
SMDS - Switched Multi-megabit Data Service
SMDS is a high-speed, packet-switched, datagram-based WAN networking technology, which is used for communication over PDN's (public data networks).
SMDS data units are large enough to encapsulate entire 802.3, 802.5, and FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface) frames.
Mobile and broadband services
ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a technology based around the concept of sending data in packets, which are of a fixed size. This technology also uses a relatively small cell size compared to others from older technologies, which in turn allows ATM equipment to transfer many types of data over one Network (i.e. Video, Audio, Jpeg) without any one type of data using all the resources. Whereas TCP/IP packets can take different routes from source to destination, ATM creates a fixed route between two points at the outset of data transfer. This makes it easier to track data usage across a Network.
When you are purchasing an ATM service, you would normally choose between these four different types of service:
CBR Constant Bit Rate - Requires the user to determine a fixed bandwidth requirement at the time the connection is set up so that the data can be sent in a steady stream. CBR service is often used when transmitting fixed-rate uncompressed video.
VBR Variable Bit Rate - Allows users to specify a throughput capacity and a sustained rate but data is not sent evenly. VBR is often used when transmitting compressed voice and video data, such as videoconferencing.
ABR Available Bit Rate - Adjusts the amount of bandwidth based on the amount of traffic in the network. ABR service provides a guaranteed minimum bandwidth capacity but allows data to be burst at higher capacities when the network is free.
UBR Unspecified Bit Rate - UBR does not guarantee any throughput levels and uses only available bandwidth. UBR is often used when transmitting delay tolerable data.
xDSL
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
The "x" at the beginning of this description signifies the whole family of technologies encapsulated by DSL. This is a fairly new technology that is still in development and is aimed at home users. Bandwidth will vary depending on the distance of the user from the Telephone company exchange. This is because DSL is distance sensitive and generally only works within a certain distance (16000 feet). The rest of the family of technologies are listed below: -
HDSL high bit-rate DSL
VDSL very high bit-rate DSL
SDSL single-line DSL
ADSL asymmetric DSL
RADSL rate adaptive DSL
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service is used as a data services upgrade to any GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) network to allow compatibility with the Internet. GPRS optimises the use of network and radio resources. GPRS has two key benefits, which are a better use of radio and network resources and completely transparent IP support.
There are a number of different GPRS protocols, some of which are:
NS - Network Service
BSSGP - Base station system GPRS Protocol
GTP - GPRS Tunnelling Protocol
LLC - Logical Link Control layer protocol for GPRS
SNDCP - Sub-Network Dependant Convergence Protocol
UMTS
Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) is one of the Third Generation (3G) mobile systems being developed. New mobile telephone technologies, such as camera phones are some of the first to feature UMTS. It is based on WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access), which is the radio interface for UMTS.
"Today's cellular telephone systems are mainly circuit-switched, with connections always dependent on circuit availability. Packet-switched connection, using the Internet Protocol (IP), means that a virtual connection is always available to any other end point in the network. It will also make it possible to provide new services, such as alternative billing methods (pay-per-bit, pay-per-session, flat rate, asymmetric bandwidth, and others). The higher bandwidth of UMTS also promises new services, such as video conferencing and promises to realise the Virtual Home Environment (VHE) in which a roaming user can have the same services to which the user is accustomed when at home or in the office, through a combination of transparent terrestrial and satellite connections. "
UMTS:
÷Provides an introduction to cellular networks and digital communications
÷Covers the air interface, radio access network and core network
÷Explains the Release '99 specifications clearly and effectively
÷Discusses UMTS services and future services beyond 3G
÷Features numerous problems and solutions in order to aid understanding
H.32x
H.323 is part of a family of ITU-T recommendations called H.32x that provides multimedia communication services over a variety of networks. H.323 is the international standard and the market leader for IP Telephony, including the market leader for IP-based video conferencing systems and IP-based long distance and toll-bypass H.323 is a standard that specifies the components, protocols and procedures that provide multimedia communication services--real-time audio, video, and data communications--over packet networks, including Internet protocol (IP)-based networks.
It is also highly regarded by companies that include Microsoft, Cisco, Siemens and Lucent.
VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol
VoIP technology enables voice transfer over Next Generation networks using protocols such as H.32x, SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) and MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol). The market for VoIP is expected to escalate at a considerable rate over the next five years or so. It is however a relatively new technology and there are many obstacles and hurdles in the way for the developers and equipment providers, who include Cisco and Netspeak. Some of these being voice quality, packet loss and latency.
Bibliography
http://www.protocols.com/
http://homepages.uel.ac.uk/u0116278/wan.htm
http://www.fbodaily.com/cbd/archive/1995/02(February)/21-Feb-1995/70sol002.htm
http://www.eg3.com/WebID/network/atm/blank/tutorial/a-z.htm
http://www.rice.edu/armadillo/Owlink/atm.html
http://www.sl.universalservice.org/reference/wan.asp
http://home.no.net/sofibos/wide_area_networking.htm
http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/22988.html
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/ito_doc/introwan.htm
http://goldey.gbc.edu/~edwarddo/148downloads/Word3/WAN.doc
http://www.erg.abdn.ac.uk/users/gorry/course/intro-pages/wan.html
http://www.erg.abdn.ac.uk/users/gorry/course/intro-pages/ps.html
http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid7_gci211787,00.html
http://www.4reference.net/encyclopedias/wikipedia/Asynchronous_Transfer_Mode.html
http://www.webopedia.com
http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com
http://www.packetizer.com/iptel/h323/
http://www.iec.org/online/tutorials/h323/
..\WAN\Data Comms PDFs\h323.pdf
..\WAN\Data Comms PDFs\x25.pdf
..\WAN\Data Comms PDFs\gprs.pdf
..\WAN\Data Comms PDFs\ATM.pdf
..\WAN\Data Comms PDFs\frame_relay.pdf
http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3485&dl=ACM&coll=GUIDE
http://www.wileyeurope.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-0470845570.html
http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/C/CSMA_CD.html
http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/T/TCP.html
http://64.4.36.250/cgi-bin/linkrd?_lang=EN&lah=38234578cd02dc252abc5998cc56f87f⪫=1070566743&hm___action=http%3a%2f%2fcomputer%2ehowstuffworks%2ecom%2frouting%2dalgorithm%2ehtm
Dick, David (2002) The P.C. Support Handbook. Kirkintilloch: