{DATE\\@ "03/22/2006"}
Student's Name: Yasser Aliyan
Assignment Type: Individual Project
Unit: 1
Course: ITN 460-0602A-01
Prof: Dr. Khaled Elleithy
Cover Page
Wireless Networking
Wireless Transmission
Personal Area Networks
find examples of devices that use radio frequency technology and those that use infrared (IR which includes the IrDA specifications IrPHY, IrLAP, IrLMP, IrCOMM, Tiny TP, IrOBEX, IrLAN and IrFM "Point & Pay"). Compare costs and capabilities. Recommend some of these devices to be used in the design of the WLAN of your local hospital.
ï· Identify wireless network architectures
ï· Research emerging technologies in wireless networking and evaluate their possible impact on an existing system
Infrared Technology
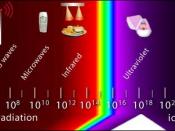
As depicted in Fig. 1, infrared radiation is the region of the electromagnetic spectrum between microwaves and visible light. In infrared communication an LED transmits the infrared signal as bursts of non-visible light. At the receiving end a photodiode or photoreceptor detects and captures the light pulses, which are then processed to retrieve the information they contain.
Some common applications of infrared technology are listed below.
Augmentative communication devices
Car locking systems
Computers a. Mouse b. Keyboards c. Floppy disk drives d. Printers
Emergency response systems
Environmental control systems a. Windows b. Doors c. Lights d. Curtains e. Beds f. Radios
Headphones
Home security systems
Navigation systems
Signage
Telephones
TVs, VCRs, CD players, stereos
Toys
Infrared technology offers several important advantages as a form of wireless communication. Advantages and disadvantages of IR are first presented, followed by a comparative listing of radio frequency (RF) advantages and disadvantages.
IR Advantages:
Low power requirements: therefore ideal for laptops, telephones, personal digital assistants
Low circuitry costs: $2-$5 for the entire coding/decoding circuitry
Simple circuitry: no special or proprietary hardware is required, can be incorporated into the integrated circuit of a product
Higher security: directionality...