ABORTION. The loss of a fetus before it is able to live outside the womb is called abortion. When abortion occurs spontaneously, it is often called a miscarriage. Abortion can also be intentionally caused, or induced. Induced abortion is regarded as a moral issue in some cultures. In others it is seen as an acceptable way to end unplanned pregnancy. Abortion is a relatively simple and safe procedure when done by trained medical workers during the first three months (first trimester) of pregnancy. Abortion is less safe when performed after the 13th week of pregnancy. Before the right of a woman to obtain an abortion was affirmed by the United States Supreme Court in the 1973 ruling on Roe vs. Wade, many abortions were performed illegally and in unskilled ways. This caused the deaths of many women from infection and bleeding. It also caused much sterility, or the permanent inability to have a child.
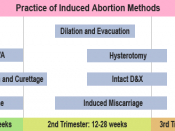
The usual surgical technique of abortion during the first trimester is to insert a metal or plastic tube into the uterus through its opening, the cervix. A spoonlike instrument at the end of the tube is used to gently scrape the walls of the uterus. A suction machine at the other end of the tube removes the contents from the uterus. This procedure is called vacuum aspiration and is done primarily in a medical clinic or doctor's office using a local anesthetic for the cervix. During the second trimester, abortions are usually done by means of dilation and evacuation. This procedure uses forceps, curette, and vacuum aspiration. Although rarely sought, third-trimester abortions may be performed when the fetus has severe genetic defects or because continuing the pregnancy would be a threat to the woman's health. A controversy began in 1988 over a drug, developed in...