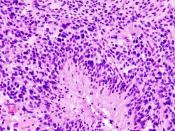
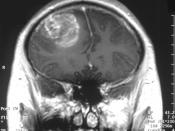
Previous investigations on glomeruloid bodies (GB) have focused on the action of VEGF. Recently it has come to light that VEGF alone in insufficient for tumour angiogenesis but involves a host of other factors. The Tie-2 receptor tyrosine kinase has been identified as the only other endothelium specific receptor and is activated through angiopoetin-1 (Ang-1). Tie-2 activation is shown to increase vessel branching, increased interaction of vessel tissue within itself and its surroundings and endothelial survival. Using orthotopic mouse models of GBM we investigated the role of Ang-1 in GB formation. It was found that Ang-1 plays an important role in GB development and resolves problems associated with GB formation induced by VEGF alone.
Background
Glioblastoma Multiforme is a Highly Invasive and Lethal Astrocytoma Brain tumours represent one of the most rapidly progressive and universally fatal neoplasms of all cancers types, affecting males more often than females1. It is estimated that in 2003, 2450 people (1350 males and 1000 females) developed new primary brain cancers in Canada, causing 900 deaths in men and 700 deaths in women.
Approximately 44% of these primary brain tumours are malignant gliomas. Gliomas are brain tumors that originate from glial cells (a type of supportive cell) in the brain or spinal cord. Gliomas include astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma and ependymoma derived from astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells respectively. Astrocytomas represent the most common group of primary central nervous tissue tumours. They are commonly classified on a grading system established by the World Health Organization (WHO) based upon the premise that each tumour type is a progressive result from a series of cellular aberrations from a preceding tumour cell type. The least severe astrocytoma being pilocytic astrocytoma (WHO grade I) and the most severe being glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) (WHO grade IV). Molecular studies have identified some...