Buño, Kathrina V. September 22, 2014
1A, Table 20
SGD 7: ANTERIOR FOREARM AND PALM OF THE HAND
Discuss the muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm.
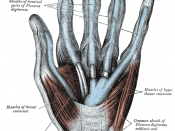
The muscles of the forearm are divided into three layers. The superficial, intermediate and deep layers. Each layer consists different muscles of the forearm, namely:
Superficial Layer
Pronator Teres
Palmaris longus
Flexor Carpi Radialis (most medial)
Fexor Carpi Ulnaris (most lateral)
Intermediate Layer
Flexor digitorum Superficialis
Deep Layer
Flexor Digitorum Profundus
Flexor Pollicis Longus
Pronator Quadratus
The muscles of the forearm have a common tendon o origin which is the medial epicondyle. Most of the muscles are innervated by the median nerve and is supplied by the radial and ulnar arteries.
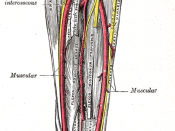
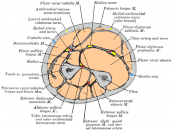
Trace the course of the radial and ulnar arteries.
Radial Artery
It is on the lateral side of the forearm.
It is the smaller terminal branch of the brachial artery.
Commencement
At the cubital fossa at the level of the neck of the radius
Course
It goes downward and laterally beneath the brachioradialis muscle and then resting on the deep muscles of the forearm.
Its middle third goes with the superficial branch of the radial nerve on the lateral side.
Its distal part is only covered by skin and fascia wherein it has the tendon of brachioradialis on its lateral side and the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris on its medial side.
Termination
It terminates by winding around the lateral aspect of the wrist.
Branches
Muscular branches
Recurrent radial branches
Superficial palmar branches
Ulnar artery
It is on the medial side of the forearm.
It is the larger artery of the two terminal branches of the brachial artery.
Commencement
At the cubital fossa at the level of the neck of the radius.
Course
It enter the palm infront of the flexor...