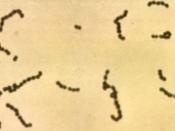Clindamycin
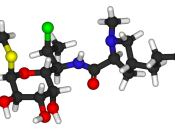
1) Chemical Name:
* methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl-trans-4-propyl-L-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamido)-1-thio-L-threo-ñ-D-galacto-octopyranoside 2-(dihydrogen phosphate)
2) Drug name and manufacturer:
* The drug name is Cleocin. Clindamycin is manufactured by several different companies which include Teuto, Ranbaxy, and Stiefel.
3) Mechanism of Action:
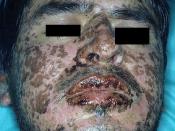
* Clindamycin is used to treat serious infections caused by anaerobic bacteria. Clindamycin is also prescribed to treat malignant infections due to strains of streptococci, pneumococci, and staphylococci. Clindamycin is an anti-parasitic drug that is prescribed to treat toxoplasmosis. Also, frequently it is used as investigational treatment for active PCP pneumonia. It also treats respiratory tract infections. If you are allergic to penicillin, or should not use penicillin according to a doctor, then clindamycin should be used specifically for these patients. Due to a risk of colitis, according to the warning on the prescription, a doctor should choose other less toxic alternatives if the infection isn't as serious. An example would be erythromycin.
To lessen the protect the sustainability of Cleocin, it should only be used to cure or prevent infections and fungi that are definitely caused by vulnerable bacteria.
4) Narrow or Broad Spectrum: Narrow Spectrum
5) What organisms is this antibiotic for?
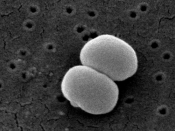
* Aerobic gram-positive cocci, including: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, when tested by in vitro methods some staphylococcal strains originally resistant to erythromycin rapidly develop resistance to clindamycin, Streptococci (except Streptococcus faecalis), Pneumococci.
* Anaerobic gram-negative bacilli, including: Bacteroides species (including Bacteroides fragilis group and Bacteroides melaninogenucus group), Fusobacterium species.
* Anaerobic gram-positive non spore forming bacilli, including: Propionibacterium, Eubacterium, Actinomyces species. Anaerobic and microaerophilic gram-positive cocci, including: Peptococcus species, Peptostreptococcus species, Microaerophilic streptococci.
6) How is it administered? Clindamycin can be administered in 3 various steps. Also, for the best results, remember to take the antibiotic on a daily basis.
* Orally
Take either with a meal or without a meal. Remember that if you are experiencing stomach pains, take with food. Taking it with a full glass of water is also optional.
* Vaginal Application
- Note that the cream can only be used in this area. It may cause burning, and above all do not have sexual intercourse while using this drug.
* Skin Application
Not to be taken by mouth. Lotion should be shaken prior to application. Remove pledget from foil and immediately throw away. Keep proper hygiene and wash hands before and after use. Apply only a thin strip of gel to avoid irritation. Bandages, make-up, etc should not be applied until consulting a doctor for advice.
7) Any toxicities, or side effects?
Abdominal pain, pseudomembranous colitis, esophagitis, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Generalized mild to moderate morbilliform-like (maculopapular) skin rashes, Vesiculobullous rashes, urticaria, have been observed during drug therapy. Rare instances of erythema muttiforme, some resembling Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and a few cases of anaphylactoid reactions have also been reported. Jaundice and abnormalities in liver function tests have been observed during clindamycin therapy. Transient neutropenia (leukopenia) and eosinophilia have been reported. Clindamycin has been shown to have neuromuscular blocking properties that may enhance the action of other neuromuscular blocking agents. Therefore, it should be used with caution in patients receiving such agents. Opposition has been confirmed between clindamycin and erythromycin. Do not take these antibiotics at the same time.
References:
1) Retrieved February 22, 2006, from MedlinePlus Drug Information Web site: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/medmaster/a682399.html#brand-names
2) Retrieved February 22, 2006, from ADAP drugs Web site: http://www.atdn.org/access/drugs/clin.html
3) Retrieved February 22, 2006, from clindamycin commonly used medication for HIV & AIDS patients Web site: http://www.hivdent.org/drugs/clindamycin.htm
4) Retrieved February 22, 2006, from Medication instructions for clindamycin Web site: http://www1.va.gov/visn10/CincyMedSheets/Clindamycin.htm
5) Retrieved February 22, 2006, from Clindamycin Web site: http://www.clindamycin.com/