Three General Network Topologies: Outline
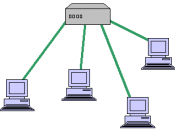
Bus:
All devices on a network are connected to a common central cable called a bus or backbone.
Generally implemented using coaxial cable during the 1980's.
The backbone functions as a shared communication.
"Networks work best with a limited number of devices" (Network Topologies, 2007).
Normally done point to point
Photo copied and reproduced from Bus Network Topology (2007).
A bus topology such Ethernet uses a single communication backbone for all devices.
Devices:
The most common type of network cable used for a bus topology is RG-58 thin net.
Maximum of 20 network devices on a segment.
Advantages:
"Less expensive than a star topology due to less footage of cabling and no network hubs Good for smaller networks not requiring higher speeds" (Falls Connect, 2007).
Relatively easy to install.
Disadvantages:
Limited in size and speed.
"A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop and can take down the entire network" (Network Topologies, 2007).
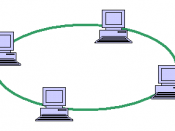
2. Ring:
Node is connected to two other nodes creating a ring.
Each device processes and retransmits the signal.
All devices have a cable home run back to the multi-access-units (MAU).
Photo copied and reproduced from Ring Network Topology (2007).
A ring topology sends messages clockwise or counterclockwise through the shared link.
Devices:
There are nine different types of cabling that can be used.
Most common type of cabling used is twisted pair.
Type 1 Shielded cable is used with IBM.
Advantages:
Network administrator or specialized network hardware can route data around the failing node.
Falls Connect (2007)⦠More reliable than the bus and star because if one node fails the network signal is passed through each network card of each device and passed on to the next device.
Disadvantages:
Relatively expensive and somewhat difficult to install.
"Network adapter...