Anatomy and Physiology IBrain Structures and Their FunctionsThe human brain is a complex organ comprised of 13 structures all with specific specialized functions. All communication from movement, emotion, thoughts, reasoning and sensations begin with the flow of signals from the spinal cord via the brain stem and onward to the brain. Each and every structure of the brain must work together in passing messages and sending messages to control the bodies functions, but each structure functions on an individual basis depending upon the action needed.
The 13 structures include the cerebrum, gyri, sulci, longitudinal fissure, Right Cerebral hemisphere, left cerebral hemisphere, cerebellum, thalamas, hypothalamus, brain stem, midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata.
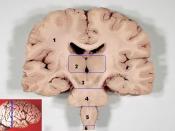
The cerebrum, also referred to as the cortex, is the upper most and largest portion of the brain. This part of the brain is associated with thoughts and actions such as emotions, memory, voluntary movements and more.
When looking at the outer layer of the cerebrum, you will notice many raised areas called gyri which are the outward folds of the brain and grooved areas referred to as sulci.
These hills and valleys provide the brain more surface area to process information.
Running laterally from the anterior portion of the brain to the posterior portion of the brain is the longitudinal fissure which separates the brain into two hemispheres, the right cerebral hemisphere and the left cerebral hemisphere. Each hemisphere of the brain isresponsible for separate and necessary function.
Communication, math, languages, reasoning, scientific skills, right hand control and all voluntary motor functions of the human body are control by the left cerebral hemisphere of the brain. Art, 3-D images, music, left hand control and imagination are all control by the right hemisphere of the brain.
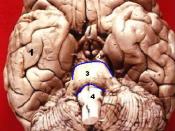
Caudal to the cerebrum, located in the posterior portion of the skull,