Classical Conditioning � PAGE �4�
RUNNING HEAD: CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
Classical Conditioning Paper
Shayolonda Herron
Learning and Cognition / PSY 390
May 3, 2010
Dr. Christa Lynch
�
Classical Conditioning Paper
Learning is a critical function of the brain. Throughout the human life span, an unending process of learning goes on. This paper will discuss the classical conditioning theory and different methods of creating conditioned responses as they relate to how you learn. Classical conditioning methods and its use in political campaigns will also be discussed.
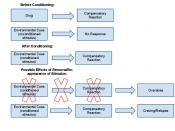
Classical conditioning involves the conditioning of a simple, automatic, inborn response called reflex (Braslau-Schneck, 2003). The focus in classical conditioning is on what happens before a response. Conditioning functions at the level of the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems (Naik, 1998). The sympathetic nervous system increases body functions, and the parasympathetic nervous system calms the body.
An unconditioned stimulus is any stimulus that has not been deliberately associated with a particular response. A conditioned stimulus requires learning to produce a response. A stimulus that does not produce a response is linked with one that does. Pavlov demonstrated this in a famous experiment in which he conditioned a dog to salivate when a bell was rung (Braslau-Schneck, 2003). Classical conditioning is separated into five conditioning processes that are critical to the definition of classical conditioning: acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination (Hall, 1998)
Acquisition is the initial learning phase of the stimulus-response relationship (Olson & Hergenhahn, 2009). The acquisition process is primarily a preparatory response to an event. The conditioned stimulus must occur a short time before the unconditioned in order for conditioning to occur. Reinforcement is any event that strengthens a response (Olson & Hergenhahn, 2009). For instance, feeding a cat that runs to the...