Theories of Motivation
Ask any person who is successful in whatever he or she is doing what motivates him/her, and very likely the answer will be "goals". Goal Setting is extremely important to motivation and success. So what motivates you? Why are you in college? If you are in college because that's what your parents want, you may find it difficult to motivate yourself. Sure, it's possible to succeed with someone else providing the motivation for you. ("If you graduate from college, I'll give you a car!" or worse "If you don't graduate from college, you won't get a car.") But motivation that comes from within really makes the difference. Theories have been developed over the years as to what motivates us and those theories are what I intend to discuss.
Compare and Contrast of Motivational Theories
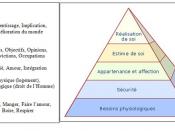
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow showed little interest in animal or laboratory studies of human behavior.
He chose instead to collect data for his theories by studying outstanding individuals. His studies led him to believe that people have certain needs, which are unchanging and genetic in origin. These needs are the same in all cultures and are both physiological and psychological. Maslow described these needs as being hierarchal in nature, meaning that some needs are more basic or more powerful than others and as these needs are satisfied, other higher needs emerge.
("Abraham H. Maslow's", 2001)
Herzberg Hygiene Theory
Herzberg found that the factors causing job satisfaction (and presumably motivation) were different from those causing job dissatisfaction. He developed the motivation-hygiene theory to explain these results. He called the satisfiers motivators and the dissatisfiers hygiene factors, using the term "hygiene" in the sense that they are considered maintenance factors that are necessary to avoid dissatisfaction but that by themselves do not...


Alright
This essay although short covers the main points needed in a essay of this title. The summary is short but could cover some more detail
5 out of 5 people found this comment useful.