The complete Biology Syllabus 2005
Section 1 Characteristics and Classification of living organism
1.
- Reproduce
- Feed
- Respire
- Grow
- Excrete
- Move
- Sensitive
- Made out of cells
2.
Nutrition: Food
Excrete: Faeces of animals, digested left over of food, waste
Respiration: Gaining energy from food
Sensitivity: Interaction with nature, feelings
Reproduction: Sexual Intercourse, production of a new cell, by union of sperm and egg to form zygote
Growth: Ability of to reproduce and replace cells
Movement: Ability to move and grow in direction wanted
2.1 (missing 2.1, 2.2, 2.3)
Extended:
Viruses: Parasite, needs other living things to reproduce, inserts into DNA, adapts to environment
Bacteria and Fungi: Need water, food, warm temperature and most of them need oxygen to survive.
Section 2 Organisations and Maintenance of the Organism
1.Cell structure
Cell wall: Protect
Cell surface membrane: Protect
Nucleus: Contains DNA, "brain"
Nuclear Membrane: To protect the Nucleus
Cytoplasm: Water (70%) many substances dissolve in it
Mitochondria: Power House of the Cell, aerobic respiration
Chloroplast: Contains chlorophyll which makes the plant green and absorbs the sunlight
Vacuole: containing cell sap (food)
Ribosome: make proteins
Starch Grain: stores the not need food
Supplement:
Similarities:
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Ribosome
- Surface Membrane
Plant cell Animal Cell
1. Cellulose Wall - No cell wall
2. Chlorophyll - No chloroplast
3. Large vacuole - small vacuoles
4. Starch granules - No starch granules
5. Regular shape - irregular shape
2. Levels of organism (missing)
3. Size of Specimens (missing)
4. Movement in and out of cells
4.1 Diffusion
-Diffusion is along the concentration gradient, for example Co2 is present in the air in a large quantity that is why it is pressed into an area with less concentration e.g. plant.
- Gaseous exchange is important to for example breath, because Oxygen is inhaled and Co2 in animals or humans is exhaled. The solute can diffuse into the solvent because water can go through every membrane whereas bigger cells cannot.
4.2 Active Transport
-Active Transport is a transport where energy (ATP) is required, this is because it is against the concentration gradient so from low to high. E.g. Root hairs force the nitrate ions out of the cell but are still able to take some of them in when they need it. It is important because the plant would die of too less ions if they weren't able to carry out active transport.
4.3 Osmosis
- Osmosis is the process in which water is forced into a region of lower concentration by the area of higher concentration.
- It is important for plants because other unwanted substances will not be able to diffuse through the membrane and so it is assured that only water is obtained. Plants will not die in pure water, whereas animal cells burst in pure water, and in concentrated solution they shrink.
- (Missing) Water potential gradient)
5. Enzymes
- Catalyst speed up a metabolic reaction
- Biological Enzymes speed up a metabolic reaction without being used in the reaction
- Enzymes are affected by temperature if the temperature reaches the optimum point about 40ð, enzymes work the best at a ph level of 7.
Supplement:
-The enzymes are important for the food industry because the production can work faster with an enzyme or it can be used to create food e.g. the enzyme pectinase is used to extract the juice from foods. Enzymes help to wash away some kinds of dirt, as well.
-The proteins that are used in the washing powders come from bacteria, which live in hot places so they survive hot temperatures in the washing machine.
6. Nutrition
- Energy, proteins etc are obtained from the nutrition. The proteins are used for example to repair cells and the energy is used to keep the body running. Carbohydrate (17kg/j per gram) or fats are used to generate energy this process is called respiration.
6.1 Nutrition
- Fats: Fatty acids, glycerol
- Carbohydrate: simple sugar
- Proteins: Amino Acids
The formation from smaller particles to bigger particles is called anabolism a form of metabolism, this is often used when substances should be stored and when need they are formed back into a smaller form by catabolism.
The Benedict solution is to test for reducing sugars if they are found the colour turns reddish, milky.
Iodine Solution is brown and it will turn black-blue if there is starch in the food.
Biuret Test is a test for proteins if it is present the colour will turn purple if not it will stay blue.
In the test for fats pure ethanol is put into the beaker and than pour only the liquid into the water if fat is present it will turn milky.
- Carbohydrates: Found in bread, cake, potatoes and rice, easy available energy
- Fats: Butter, lard, margarine, oil Storage of energy (39kj/g) insulation
- Proteins: Cheese, Fish, eggs, peas making cells, antibodies, emergency energy (17kj/g)
- Vitamin C: Oranges, Lemons, potatoes keeps tissues in good repair
- Vitamin D: Butter, egg yolk, can be produced by the skin when sun shines on it, helps calcium and phosphates to be used for making bones.
- Calcium: Milk, cheese bread for bones and teeth
- Irons: Liver, egg yolk, haemoglobin
- Fibre: Plants contains roughage, cell wall, this keeps the alimentary running because of the contraction and relaxation
- Water: Water, dissolves substances needed for metabolic reactions.
Deficiency
Vitamin C: Scurvy causes pain in joints
Vitamin D: Rickets bones become soft
Calcium: Brittle bones and teeth
Irons: Anaemia not enough red blood cells, small energy supplies shortage of oxygen.
Supplement
-The yeast is used to increase the size of the bread by respiration of the use of CO2, yogurt is made by lactose? lactic acid + energy, coagulate, curds, whey is produced. The use of bacteria and other substances are important to create new tastes.
- Benefits for producers is to improve the product by changing the DNA, many sweets are coloured to create a good look, for example a special orange is produced, which can produce more juice this increases the output of the business, but often in genetic changed products more vitamins but also life threatening substances are included.
6.2 Plant nutrition
6.2.1 Photosynthesis
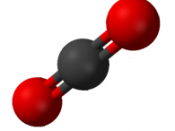
Photosynthesis is the process in which plants produce oxygen and energy by using water + carbon dioxide
Sunlight
Carbon dioxide + water ? glucose+ oxygen
Chlorophyll
- The mesophyll layer absorbs energy form the sunlight, the energy gets trapped inside of the chlorophyll and than the energy is stored in the form of ATP inside the mitochondria the energy is produced by the release of energy from the glucose. The ATP is than used to carry out any other metabolic reaction inside the plant e.g. grow, produce proteins.
Supplement
- There are three limiting factors, the sunlight, carbon dioxide, and stomata. If there is a lot of the sunlight photosynthesis will happen more often and quicker. If there is a higher concentration of carbon dioxide in the air the plant will be able to carry out more photosynthesis. The last limiting factor is the stomata; if the temperature is too high the stomata will be closed to prevent water loss, so the temperature should not be too high to assure a good rate of photosynthesis.
- In the greenhouse it is very important to assure an optimum because if the plant has everything it needs to produce photosynthesis at a high rate and so produce a lot of oxygen.
6.2.2
Distribution of chloroplast: The chloroplast is in the meosphyll layer to provide enough protection by the upper epidermis and still absorb the sunlight very effectively, that is why in the lower epidermis is nearly no chloroplast so the sunlight reaches only the mesophyll layer.
Stomata and mesophyll cells: these cells provide gaseous exchange through the spongy layer, oxygen is produced and leaves the stomata and the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the spongy layer by the palisade layer.
Xylem and Phloem: The xylem carries water through the plant from the roots, and the phloem transports food in form of glucose through the plant.
6.2.3 Minerals requirements
- Nitrates ions are important to create proteins, which are need by the plant to carry out metabolic reactions
- Magnesium are important to create chlorophyll which are needed for photosynthesis
- Nitrogen is used to make the plants grow faster if there is too much fertiliser in the soil it will sink into the ground water in infect it, this will causes diseases. It takes years for the water to become clean again.
Supplement
- Magnesium: yellowing between veins of leaf
- Nitrate: poor growth, yellow leaves
6.3 Animal nutrition
6.3.1
A balanced diet for each day should include carbohydrates, minerals, water, roughage, proteins, fats, and vitamins.
- The diet must fit to every person, a person, who excises a lot need more carbohydrates, than a person, who does not. A older person should eat less fats because it can cause coronary heart diseases, a fat person could be easier target to it. Obesity is caused by too less exercise and eat too much.
- Alcohol can make addictive and damages the liver, destroys brain cells, and neurones influences the coordination system (cerebellum)
Social conflicts, leads to crimes to get the alcohol tendency to violence when misused.
Supplement:
The problems of world food supplies, in some countries of this world there is not enough food because the agriculture condition do not allow a great range of different foods. And so people often suffer from famine because they have nothing to eat whereas in other countries people have no problems with food supply and eat so much that many people are fat.
6.3.2 Human alimentary canal
Ingestion: Is the process in which food is taken up, food into the mouth
Digestion: Is where the food is broken down
Absorption: Minerals are absorbed in the stomach and in the small intestine
Assimilation: The food is separate and the still need food is taking up for example in the liver.
Egestion: Food, which could not be used by the body, is removed
- Mouth, tongue, stomach, small intestine, rectum
6.3.3 Mechanical and physical digestion
- Mechanical digestion: Incisors are chisel shaped, for biting off pieces of food
- Canines: are similar to incisors in humans
- Premolars have wide surfaces for grinding food
- Molars like premolars are used for grinding
-- Plague causes tooth to decay, which is caused by bacteria
- Don't eat too much sugar
- Use fluoride toothpaste regularly
- Visit to dentist
--
- In the process of chewing bigger pieces are broken down into smaller pieces and they are formed into bolus
- Peristalsis is the contraction and relaxation of the alimentary canal to push down the food. Wave-like movement
Supplement
- The fluoride prevents the bacteria to sit on the tooth and so prevents plague, if there would be fluoride water people would get too much if they want to drink a lot of water, than people would turn immune to it like with antibiotics.
6.3.4 Chemical Digestion
- Amylase breaks down the starch to Maltose
- Protease (trypsin) breaks down proteins to Amino acids
- Lipase breaks down emulsified fats into fatty acids and glycerol
6.3.5 Absorption
- It is very long 5m in an adult plenty of time for digestion
- Has villi with microvilli enlarge surface
- Villi contains blood capillaries food into blood, direct use, amino acids sugar
- Lacteals, part of lymphatic system fats absorbed
- Villi only 1 cell thick fast absorption
- Villi has goblet cell which makes mucus
Supplement:
- Hepatic portal vein transport all the food directly to the liver where it is broken down, stored, filtered or carried further on through the body
6.3.6 Assimilation
Glucose dissolves into the blood plasma, is then taken to other parts of the body, where it may become assimilated as part of the cells. Fat is broken down in the liver and than it is carried with the blood, if the energy is need if not it is stored. The destruction of amino acids happens by the removal of the excess in the urea.
Supplement
- Deamination is the process in which the left over nitrogen is turned into urea and carried to the kidneys to be excreted. The amino acids dissolve into the blood and are taken to places in the body, which need energy for metabolic processes.
7 Transportation
7.1 Transport in plants
- The root hairs take up minerals and water from the soil and transport it through the stem to the leaves along the xylem.
7.1.2 Transpiration
- Transpiration is the evaporation of water from the leaf
- The water loss is related to keep the plant moist and so every cell has enough water and wont dry out.
- Temperature will increase the transpiration because more water is needed, and so a higher water consume, also the light intensity when high will cause the rate to increase and the rate of transpiration will drop when the surrounding has a high humidity.
Supplement
- The water is pushed from the roots upwards through the xylem that is why the water reaches the areas because if water is need it is pushed upwards.
- The leaf can be big or small, in a wood with a lot of shadow the leaves will be big and in areas with a high light intension will have small leaves, the steam will be very thick in areas where there is a fast wind, in areas were there a less storms the steam will be thicker, also the roots will be very deep when the plant is big e.g. a tree or in areas with extreme wind conditions.
7.1.3 Translocation
- Glucose is a simple sugar and so can transport by the water, when it reaches the mitochondria the glucose is formed together with other to form a complex sugar, starch by the process of anabolism.
Supplement
- Chemicals are transported on the same way as the other because they are also transport with the water in the plant and so it goes through the plant and so the e.g. substances which should increase the growth will reach the areas like the glucose and will not be stored but used up very quickly, pesticides are extracted when the plan by accident absorbed it form the surface.
7.2 Transport in humans
- Through exercising the body need to support more oxygen to the places where it is need to carry out respiration this results in a faster heartbeat and pulse.
- Heart attack
- Can be cause by smoking because the carbon monoxide combines with the haemoglobin in the blood and so, there is no space for the oxygen anymore so the person will get less oxygen and will run out off breath quickly.
- It can also because by a wrong diet because to much fat will clot the blood supply to the heart, this means less oxygen is supplied to the heart
- A healthy diet can prevent a heart attack, and so does a stress releaser like sports or to keep the body working. No smoking either.
7.2.2 Arteries, veins and capillaries
7.2.3
(Missing)
8. Respiration
Is the process in which energy is released from food.
8.1 Aerobic Respiration
- Aerobic respiration is the process in which oxygen and glucose are transformed into energy, carbon dioxide and water. Oxygen+ Glucose ? Energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, water
- The energy is used for metabolic process for example, storage of food, break down off food, homeostasis etc.
8.2 Anaerobic Respiration
- Anaerobic Respiration is the process in which oxygen ? less energy + ethanol or lactic acid and carbon dioxide
- Yeast respires when it is in the e.g. the bread and so creates dough with carbon dioxide inside, which was released by the anaerobic respiration. Through anaerobic respiration lactic acid is produced and this is located in the muscles, this happens when there is no more glucose for aerobic respiration.
8.3 Gaseous exchange
- Thin
- Close to transport system
- Moist
- Large surface area
- Good supply of oxygen
Inhaled Exhaled
Oxygen 21% 16%
Carbon 0.03% 4%
Nitrogen 78% 78%
- Lime water changed to milky when carbon dioxide dissolves in it
- Hydrogen carbonate indicator changes it colour from red to yellow when carbon dioxide dissolves
- The person will start breathing faster and the heart beat increases to supply the body with the oxygen needed, and so also with the glucose as long it is there.
- Tobacco contains the tar attaches to the alveoli in the lung an helps the lung to produce more cells which causes cancer, the carbon monoxide in the smoke attaches to the haemoglobin in the blood and so can cause oxygen depth because there is less space for it.
Supplement
- It is the movement of diaphragm and the contraction of the intercostals muscles. The diaphragm contracts and this pulls it downwards, the volume of the thorax increases. The intercostals muscles contracts, this pulls the rib cage upwards and downwards. Together this increases the volume of the thorax. When breathing out, the diaphragm springs back and pushes the air out.
9. Excretion in humans
Supplement
- Dialysis is the process in which the kidney get ride off the urea, which is filtered, in the kidney.
- The transplant might not work as efficient as a dialysis but it will not take so much time for the patient and he does not have to go the hospital, but the implant kidney might not he as efficient but it will be acceptable if the person does not drink a lot of alcohol or eats too much fats the reabsorbed substances will be enough.
10. Coordination
10.1 Hormones
- Nerve messages can be carried without an impulse; these messages will be carried with hormones. Chemical substances released by the endocrine system. Little amount of hormones.
- Adrenaline controls the preparation for fight or flight, the reflexes becomes faster, hard beat increases, faster breathing the pupils widen.
Supplement
- Auxin is a hormone, which helps the plants to grow too much of these will cause the plant to grow unnatural. Weed killers will also contain substances, which will kill other plants, and these might be toxic and will sink into the ground water and poison it.
- Hormones in food like auxin will increase the size of the plant, which would be very useful to create bigger plants but this will cause genetic problems and the plant will contain chemicals, which in greater amount might cause diseases.
10.2 Tropic and Taxic responses
- Geotropism is the movement towards or away from the earth
- Phototropism is to or away from the sun
- No directional response they always move away from the ground. They follow their instinct. E.g. earthworm and pencil.
Supplement
- The growth rate is influenced by auxin but the sun, with a plant, influences the direction for example. It grows towards the sun.
10.3 Nervous control in humans
- Nervous system, made up of neurons. 2 types CNS brain and spinal cord, Brain: passing messages/ impulse to the rest of the body by PNS
- Eyes: Photoreceptors
- Skin: Thermo receptors
- Nose: Chemoreceptor
- Ears: Mechanoreceptors
-Tongue: Chemoreceptor
-Sensory neuron: impulse affecter organ from skin receptors to spinal cord
Motor neuron: response spinal cord to muscle effectors organ
- Antagonistic muscles, opposite reaction Biceps and Triceps
-If your hand touches a hot plate the sensors at your hand send a message to the spinal cord, which then send the massage to the brain. The brain processes the information and relies that the high temperature is harmful for the body and immediately sends a massage back over the spinal cord to the muscles at the hand, to contract, so that the arm is pulled away from the source of heat.
-Muscle attaching eye to skull: to keep the eye in place and to give the eye the ability to move in different directions
-Conjunctiva: thin layer that covers the eye, it is always kept moist, moisture contains enzymes that can kill bacteria
-Cornea: bends most of the light
-Iris: protects the pupil and lens
-Lens: makes fine adjustments of the light
-Aqueous humour: protection of the eye
-Ciliary muscle: stretches and relaxes the lens, so it can adjust to the light
-Suspensory ligament: holds the lens in position
-Sclera: protect the eye, tough surrounding
-Fovea: contains receptor cells
-Blind spot: no receptors cells at this place, if light falls on there no message is send to the brain
-Choroid: absorbs the light after is past the sensors
-Rods and Cones: photo receptors, cones black and white, and rods colours
Pupil: Adjust the amount of light vitreous humour
- Nervous system is only mend for fast, little, complex messages and the hormonal control system is for simple, long-term commands, e.g. thyroxin.
Supplement
-Involuntary action is a reflex action as pulling the hand away from fire and voluntary action is something you planned to do, e.g. lifting a plate
10.4 Homeostasis
- Homeostasis is the process, which keeps the internal temperature constant despite outside effects.
- The temperature is checked if it is too high, a message is send to the hypothalamus, which sends a message to the sweat glands, that they should secret sweat, this will lead to a cooling down, if the temperature drops to low, the negative feedback loop engages and tells the hypothalamus to stop the gland. Vasodilatation is when the veins under the skin widen to let more blood through it to, when it is hot; so more water can be lost through sweating. Vasoconstriction is when the veins degrees in size so less blood it supplied to the skin to prevent the loss of heat.
Supplement
- The liver "checks" the amount of glucose in the blood if it rises above normal, it send a command and the pancreas secret insulin which control the amount of glucose in the blood, the insulin tells the liver to store the glucose.
- Negative Feedback control the amount of anything in the body if it rises above normal or under normal the negative feedback will engage the opposite process to prevent it from sinking, or rising further.
10.5 Drugs
- Alcohol can make addictive and damages the liver, destroys brain cells, and neurones influences the coordination system (cerebellum)
Social conflicts, leads to crimes to get the alcohol tendency to violence when misused.
Heroin can lead to the same consequences but has different effects; it is inhaled or injected into the blood stream
- Die of an overdose - Effect on Hypothalamus; brain higher blood pressure, aggressive. Social problems ostracised.
Section 3 Reproduction
1. Reproduction
1.1
- In an asexual reproduction an identical copy is produced from the one parent in a very short time.
- Bacteria reproduced by a process called binary fission, Fungi will create a outgrowth such as the tuber will.
Supplement
- The advantages of asexual reproduction is that it can happen very quickly and no other organism is needed for this, but this also causes problems the evolution will not happen very fast and only by accidents, for example changes in the genetic level by for example radiation.
1.2 Sexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction involves two organisms, the union of an egg and sperm, which will result in the formation of a zygote.
Supplement
The advantage is that if two strong animals reproduce a stronger animal will be created and this called evolution, the disadvantage is the time and sometimes the problem if male and female don't meet.
1.2.1 Sexual reproduction in plants
- The arrangement of the vascular tissue in a plant stem differs in dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. In a typical dicotyledonous plant stem the vascular bundles are arranged in a circle in the middle of the stem surrounding central pith. To the outside of the vascular bundles is the cortex, which is covered by a single layer of epidermis cells. The xylem of the vascular bundles is orientated towards the middle of the stem and the phloem towards the outside.
-The travel of the pollen from the male gamete to the female gamete is called pollination.
- The insect pollination is for area where there is only a low wind, and for small flowers because the seeds will not fly as far and if many plants grow around this plant there will be a food shortage.
Wind-pollinated flowers are for big areas where fewer animals would take up the gametes.
- Dispersal of seeds means the spreading of the seeds, fruits are ovaries after fertilisation, they can be identified by two ways a) it has more than one seed b) two scars.
- Animals eat fruits and they carry it away and somewhere they extract the seeds will find a new place to grow, whereas wind dispersal is when seeds are carried by the wind to new areas.
1.2.2 Sexual reproduction in human
- Sexual intercourse: two gametes meet (sperm and egg) and form a zygote by the process of fertilisation.
- Implantation: zygote sinks into the thickened lining of the uterus ? excess blood flow, glucose, and amino acids.
- Placenta: disc shaped organ, the connection between mother and child (filter)
Supplement
-Amniotic sac is filled with the amniotic fluid this is where the baby swims in it get its food and excreted its faeces in it.
- Breast-feeding is better because the mother has more minerals and other substances in her milk that the baby need at the beginning it is advised to feed the child till the 7-month with the breast milk.
1.3 Sex Hormones
- Female Male
On set of menstruation shoulders broaden/muscular
Breast starts to grow Voice change
Hips broaden facial growth
Sex drive production of sperm
Increase growth sex drive
- FSH stimulates the development of a follicle
produce Oestrogen
- Oestrogen lining of the uterus becomes spongy, secretion of endometrial
- LH: cause ovulation ? corpus luteum, release progesterone.
- Progesterone: maintain endometrial lining, prevent secretion
1.4 Method of birth control
Natural: Rhythm, count days, mid cycle no sexual intercourse, not reliable
Removing Penis before ejaculation Coitus erectus
Mechanical: Condom (Male), Cap (Female) Inter Uterine Device inserted into uterus
Chemical: Spermicidal Gils: coated in vagina destroy sperm. Contraception Pills, Oestrogen Progesterone increase.
Surgical: 100% reliable, permanent sterilisation, Vasa defentia are tied, vasectomy
Fallopian tubes tied Tubectomy
Uterus is removed Hysterectomy
Supplement
Insemination causes a lot of problems because female can get pregnant without a man, that is not seen as very lovely way in society and the child has only a mother in most cases. Hormones in fertility drugs can cause distraction and problems in the body when too much in the body.
1.5
- Male: yellowish discharge from the penis and pain when passing urine after a week
- Female: burning when passing urine can cause (PID) infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease.
Transmission through oral, anal gentile sex
Treatment: Antibiotic injection
Prevention: Condom, checks with doctor
--
HIV is transmitted through sexual intercourse, or through contaminated blood( Rhesus monkey) prevent through condom during sexual intercourse.
Supplement
HIV infect the immune system, it sits on the helper cell and infects the helper Tcell that produces antibodies against any viruses.
2. Growth a development
- Growth is the increase of cells in the body by the hormone called thyroxin.
- Development is the increase of knowledge and the growth of the brain and nerve cells
- The environment has to be optimal for the plant the most plants adapt to the surrounding e.g. big or small leaves etc. For example strong winds will destroy small plants.
3. Inheritance
3.1 Chromosomes
Chromosomes: in nucleus of a cell
- Long thread like structures
- Are visible through a light microscope when thick
Gene
- present inside chromosomes
- carry genetic information
Allele
- 2 forms of a gene, (correct, incorrect)
Haploid
-A sperm or egg has only 23 chromosomes; of each kind this is called a haploid cell
Diploid
- When tow gametes fuse together they from a diploid cell.
--
Dominant alles are the features, which are inherited and seen
3.2 Mitosis
- Mitosis is the process in which one cell creates an identical copy of itself, asexual reproduction.
3.3 Meiosis
- Cells in e.g. testes divide and form a gamete, a cell with half the amount of chromosomes (23)
3.4 Monohybrid inheritance
Allele
- 2 forms of a gene, (correct, incorrect)
Genotype
- responsible for phenotype
Phenotype
- a visual feature
Homozygous
- 2 same allele (TT)
Heterozygous
- 2 different allele (Tt)
Dominate, Recessive
Supplement
- Codominance is when both alleles have an effect on the feature of the organism
+A- Ia Ia / Iai
+AB- Ib Ib / Ib i
+B- IaIb both codomiance
+O- ii
3.5 Variation
- Discontinuous: NO or YES
- Continuous: no 2 extremes but a range of a particular trait
- Define Mutation: random changes in trait
Change at genetic level/ in DNA or chromosome, most mutation harmful
- No disjunction at chromosome 21, has three chromotids (Down's Syndrome)
- Constant exposure to chemicals and radiations speed up mutation causes non-disjunction
Supplement
- Anaemia is caused by an deficiency of irons whereas malaria is caused by a mosquito, so the one is caused by an deficiency the other one through the blood.,
3.6 Selection
- The artificial selection is important because only the best fruits or animals are taken to reproduce another better generation, this will great a better plant and so only the strongest survives.
- The best animal survives in the end, and so a better generation is created through the natural selection of the best genes.
Supplement
- If always the best survives the generation will lose their weakness and gain strengths that will lead to perfection and evolution.
- If bacteria were killed by antibiotic, the bacteria left over will remember it and adapt to the antibiotic. That is why you should not use the antibiotics so often.
Genetic Engineering
Supplement
- The insulin is extract from the body of a human, an enzyme is used to chop the DNA in smaller pieces, and the particular piece with the code for making insulin is identified from the rest. Now the code is taking and put into a bacterium, by a process called plasmid. Genetic Engineering technology is very important.
Biology Section IV
1. Energy flow
-
The sun is the principal source of energy to the biological system, plant need it to carry out photosynthesis, and human need it to create a special vitamin, that need sunlight to be created.
Not only the energy is need in form of radiation, but only the warmth, through the sun. Without the sun we would still have an ice age, so do some plant need a special climate to survive, for example plant in the rainforest need a moist air. Human life can only exist because of the sun, it gives warmth and energy, which plant need and we need the plants to produce air, it like a cycle were the start is the sun.
-
The nature of non-cyclical of energy flow is because many factors must match to allow energy flow to happen. For example a rabbit eats grass so he picks up the energy, there are times where the rabbit has to eat, but if there is no grass the energy flow cannot start.
2. Food chains and food webs
-
Food chain: All living organism need energy and they need get thought food, respiration, the food chain starts with a producer e.g. Gras?Rabbit?Fox, always it start with a plant
Food Web: are more complex and contain more information they are larger and show a wider range of animals and how they are connect with each other
Producer: Plants, the start of every food chain (web)
Consumers: The organism that eat the plants, and so gain their energy from them or from other animals, the consumers cannot produce energy by themselves.
Herbivore: Organism that feed on plants, (plant-eater)
Carnivore: Organism that eat other animals, (meat-eater)
Decomposer: Gain energy from dead organism
Ecosystem: a system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment
Trophic Level: means feeding, every level of a food pyramid is called trophic level.
-
With every trophic level the energy get less so if you go higher there is less energy, because all animals in this pyramid feed on one source, so the gained energy is shared and some is kept back, so with a higher pyramid there is very less energy left on the top. A small food chain is so better because the energy gained from it is higher and so the pyramid is smaller and energy does not have to be shared.
-
A pyramid which described by its body mass will be upside down, because the producer has the highest mass and the last one on the pyramid the smaller. Biomass is the mass of the organism. The number of animals feeding on one pyramid is important to see the importance of the producer e.g. grass. How much the energy the animal need can be also shown in a diagram to see how much it needed of the producer e.g. grass.
Supplement - Humans need more vitamins and so absorb them from the plant, animals cannot absorb the food as efficient as a human, also the energy provide by the plant can be released much quicker by the human than by the animal, animal need different sources of food for example meat, which gives them more energy. Human can gain much more from plants than the animals.
3. Nutrient cycles
Carbon cycle is the waste product of an organism and the source of energy for plant to carry out photosynthesis, which produces oxygen and so the animal can breath in oxygen and out carbon and so the cycle starts gain.
Water cycle can start with ocean, since it is a cycle you cannot tell where it starts, the water evaporated and goes into the air where it cools down and forms a cloud, the cloud rains onto the ground, for example a forest and the plant take up some of the water, the rest sinks into the ground water, the human is also a consumer of the water, which is excreted in the urine. The water collects some where in the open again and evaporates.
Supplement -- Nitrogen cycle; living organism need nitrogen to produce proteins, there is plenty of nitrogen in the air, 79%, but in a very unreactive form to be more reactive it must be changed into a different form such as ammonia or nitrates. This called nitrogen fixation
Lightning: makes some of the nitrogen gas in the air combine with oxygen, now they are called nitrogen oxides, it washes into the ground where they form nitrates.
Artificial fertilizers: Nitrogen and Hydrogen can be combining through industrial chemical processes forming ammonia. Ammonia is used to make fertilizers.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria:
These bacteria live in soil or root nodules, they use nitrogen gas from the air spaces in the soil and combine it with other substances to make nitrates,
Supplement - When more fuels are burned more carbon is produced, which changes the balance to much carbon dioxide will not be able to be used by plant since not all carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can be used and it gets more. The rainforest the greatest resource for our oxygen supply is being cut down and so even less oxygen can be created, this will cause a lot of problems in our future. More carbon dioxide, less oxygen will cause a lot of death.
4. Population size
-There many affects that effect on the population size, food is one of the most important reasons, where there is no food people cant live, they need import or help from other countries or need animals to kill for food. Food is important so is fresh water supply, infected water my cause diseases which kill the population, also the location is important near to danger zones, like volcanoes or the danger of hurricanes. The affects might cause death or just a smaller growth rate. Also the stage of development is important so people in very far countries often have more old people and less children because they want to care about their carrier, and in not so developed countries there oft to many children to feed and to less food.
- A limiting factor like food will lead to a decrease of the population and so the curve will go down, the culture will engage the growth phase much later, than countries if enough food.
(The Sigmoid curve was not in the book, so I tried to guess the question)
- The population is growing, that is for sure. Although in countries like Germany less people have children, the population is growing very rapidly, in China every year the population grows by one million. China and other countries have huge problems with such growth, to provide work and resources. This can cause famine and social problems because people are getting poorer. Social problems also can lead to the reduction of the growth rate, people take more care about their carrier and so the family stays in the background, so materials like oil are more produced to keep up with the supply and someday we will have no more oil left. Also living space is a problem in for example Japan, where people have to live on the smallest amount of space. In China people are not more aloud to have more than one child without permission from the sate, and this will continue because the world is growing.
- (The last question of the syllabus says, " interpret graphs and diagrams of human population growth", I understood it more as an advice and did not see the question. If I am wrong I will try to make it up.)
5. Human influences on the ecosystem
5.1
Through modern technology, more food needs to be produced, but why? People life longer because of technology and science, this means these people need more food in their life, because their life span is much longer, than in countries that are not developed. The technology helps people to produce more; new machines make it easier to produce more in less time. Through a better water supply the, areas which were dry and not use before, can now be sprinkled with water and fertilizer so more areas can be made productive. Also the state gives farmer that produce a special kind of vegetable or fruit extra money this process is called subsidy.
Deforestation has many side effects, for example through the deforestation trees are cut down and so less oxygen is released, also the total amount of trees reduce and so in the end the trees might extinct. Through the destruction of the woods, also the living space of animals is destroyed.
Fertilizer can help to increase the amount and the quality of the food by killing virus, but by to using too much of these chemicals the crop can be damaged and people, who eat it later on, might get sick because of the unhealthy chemicals.
5.2
Sewage in rivers can cause harmful diseases; this is why it needs to be treated before it is released into the river. This is the same with chemicals. ,
Sulphur is very harmful to the environment it is produced by cars, when they burn to the fuel or by coal factories. Sulphur can travel many km with the high air so prevention can only occur in the factory by using filters. Sulphur washes out the ions in the soil and so plants have less of these important minerals to absorb and so die, the aluminium and other ions maybe washed into rivers, where fish might die of the ions.
Supplement -- The significations of non-biodegradable and other materials used in destroy is that; these materials will not be able to be recycled, which make them useless in the end, like atomic waste. Atomic waste is burrowed in the see or in hills. Someday there will be no space left, and so we must develop a method to recycle waste like plastic.
Supplement -- Acid rain kills plants and other animals indirectly. For example Sulphur it is carried over long distance with the high air, so it makes no sense to try to help the area of plants, it needs to be stopped in the source. The process of burning releases Sulphur and nitrogen, and so cars and factories produce these gases which are very harmful to the environment, Sulphur washes out the ions in the soil and so plants have less of these important minerals to absorb and so die, the aluminium and other ions maybe washed into rivers, where fish might die of the ions.
5.3
The importance of conservation of animal and their environment is clear. Life is a circle if you talk out one part it gets smaller and other parts also fall off. In the food pyramid animal depend on their food or their pray and if this dies they will soon die and other will die and so a wave starts and continuous on and on.
Supplement -- The sewage must be filtered out of the water and this is happens in a settlement tank, were the sewage sinks to the ground and then it the sewage is taken away or absorbed to be cleaned and this can happen by organic needs, for example by other bacteria that kill the "sewage bacteria". Paper can be recycled by putting all the paper into a tank where water and some chemical substances dissolve it again into liquid form, the paper is then filtered again to filter any other material than new paper is made from it.