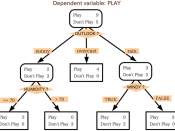
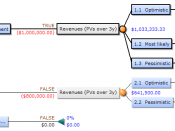
Decision-making takes place against a background of uncertainty about the future course of events. Consequently, in making decisions known costs are compared with expected pay-offs in the future. Decision trees provide a logical process for decision-making. The decision problem can be set out in the form of a diagram, like a tree on its side. It can take into account the occasions when chance will determine the outcome. Chance can be estimated by assigning probability. While the estimate of the probability may only be a guess, at least probability is quantitative and gives the decision process a scientific quality.
The kinds of problems which are suited to decision tree analysis are those where a sequence of events or options has to be followed in conditions of uncertainty. The types of decisions that lend themselves to the decision tree technique include:
Whether to introduce a new product or continue with existing products;
Whether to launch a new advertising campaign or continue with existing products;
Whether to sell off assets for a known price or continue to use them in conditions of uncertainty;
Whether to expand in one location or another.
The decision tree allows for uncertainty/chance, which makes it a better model of the reality of an uncertain business world.
Advantages of Decision Trees
Decision trees set out problems clearly and encourage a logical approach. The discipline of setting out the problem in a decision tree requires logical thinking and can also generate new ideas and approaches.
Decision trees encourage a quantitative approach and force assessments of the chances and implications of success and failure.
Decision trees not only show the average expected values for each decision but also set the probability of a specific outcome occurring.
Decision trees are most useful when similar scenarios have occurred before so that good...