Gout
Gout is a complex disease of uncertain origin caused by the faulty metabolism of uric acid produced in the body by breakdown of protein, and resulting in elevated levels of uric acid. Gout has been studied by physicians and has caused suffering to many people. Formerly a leading cause of painful and disabling chronic arthritis, gout has been all but cured by advances in research. Unfortunately, many people with gout continue to suffer because knowledge of effective treatments has been slow to spread to patients and their physicians.
An excess of uric acid in the body creates gout. This excess can be caused by an increase in production of the body, by under-elimination of uric acid by the kidneys or by an increased intake of foods, which contain purines, which are metabolised to uric acid in the body. Certain meats, seafood, dried peas and beans are also particularly high in purines.
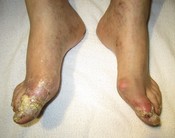
Drink's containing alcohol may also increase uric acid levels. With time, high levels of uric acid in the blood stream may lead to deposits around joints. Eventually, the uric acid may form needle-like crystals in joints, leading to acute gout attacks. Uric acid may also collect under the skin as tophi or in the urinary tract as kidney stones. Repeated attacks may result in the development of a condition known as chronic tophaceous gout. In this condition crystals of uric acid lodge as white, chalky material in soft body tissues and in and about the joints, where they may cause bursitis and destruction of bone. Large and deforming deposits may, after many years, settle in the outer margins of the ears, a characteristic feature of the disease. Chronic gout may also cause kidney damage by the formation of uric acid stones, a condition called urate, or gouty, nephropathy.