DETERMINATIONS OF THE PROTEIN CONCENTRATION OF A CELL EXTRACT USING THE 'BRADFORD METHOD'.
CBDP2
1LFS0028
PRACTICAL GROUP E
14TH OCTOBER 2008
ABSTRACT
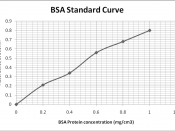
The aim of the experiment is to find out the concentration of cell extracts (Bovine Serum Albumin, BSA) using the Bradford method. Stock solution of BSA was made by diluting the protein solution to prepare concentrations ranging from 0.0mg/cm3 to 1.0mg/cm3 (Peck, 1998). 5cm3 of the Bradford dye reagent was added to 100ül of the solution and allowed to stand for 28mins. The absorbance of each solution is measured at 595 nm with the following results: 0.00 mg/cm3 = 0.00, 0.2 mg/ cm3 = 0.21, 0.4 mg/ cm3 = 0.34, 0.6 mg/ cm3 = 0.56, 0.8 mg/ cm3 = 0.68, and 1.0 mg/ cm3 = 0.80. The values of the absorbance were plotted against protein concentrations and the resulting line was used to calculate the concentrations of the unknown samples and the aim was achieved.
INTRODUCTION
Protein concentration determination of samples is very necessary and it's often used i.e. to know the amount of protein available in a sample. Various methods for determining the protein concentrations in a sample are available but vary in ease of use, cost, and sensitivity. The most commonly used methods are the Bradford assay, Lowry assay and the BCA assay. In this case, the Bradford method, which is a dye binding method, is used. It is faster, cheaper, and more sensitive, does not require heating, and has fewer mixing steps than the other methods above.
This method is based on the binding of protein to a dye, leading to a shift in the absorbance maximum of the dye used. The dye, Coomassie blue, has a maximum of 464nm but when it binds to a protein, the maximum shifts to 595nm. After...